| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
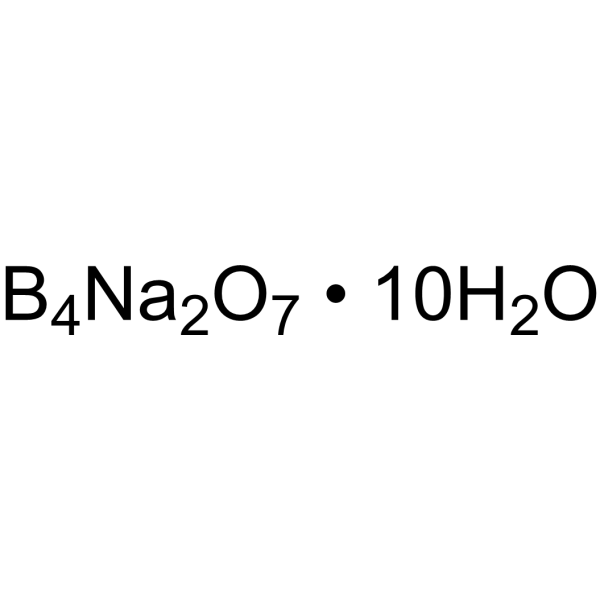 |
Borax
CAS:1303-96-4 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
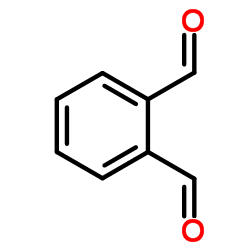 |
o-Phthalaldehyde
CAS:643-79-8 |
|
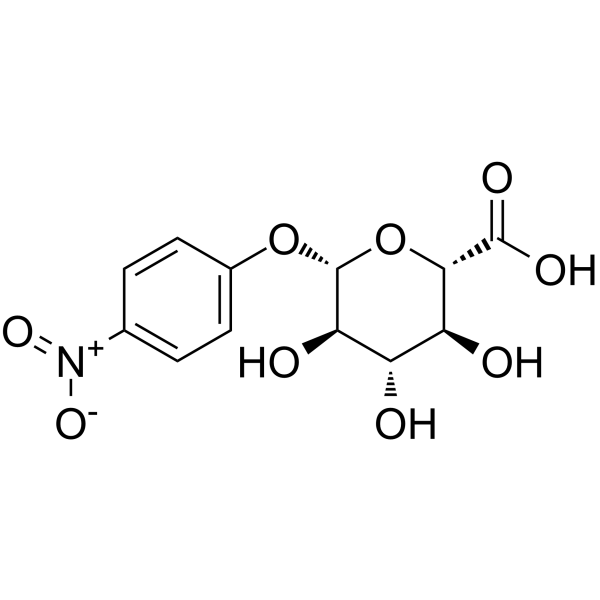 |
4-Nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid
CAS:10344-94-2 |
|
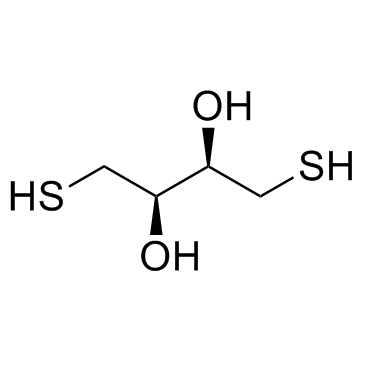 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
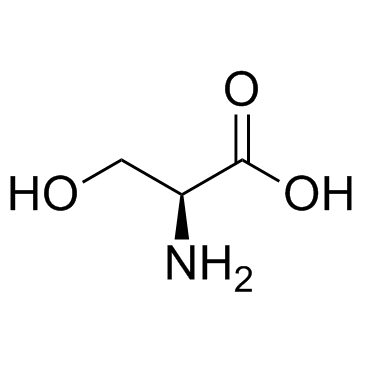 |
L-serine
CAS:56-45-1 |
|
 |
Pancreatin
CAS:8049-47-6 |
|
 |
Pepsin
CAS:9001-75-6 |
|
 |
Hemoglobin
CAS:9008-02-0 |