| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
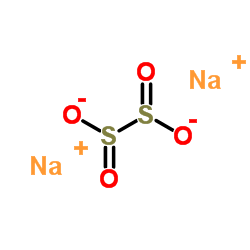 |
Sodium dithionite
CAS:7775-14-6 |
|
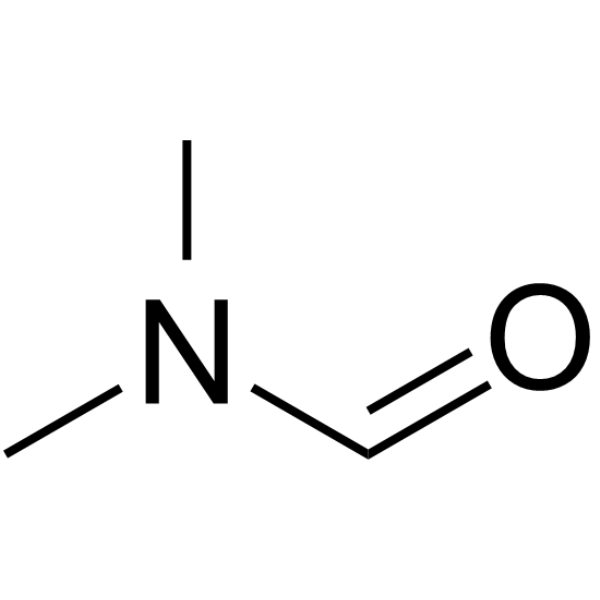 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
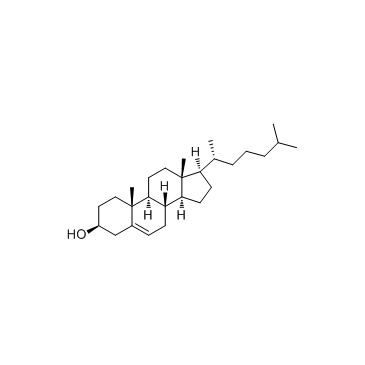 |
cholesterol
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
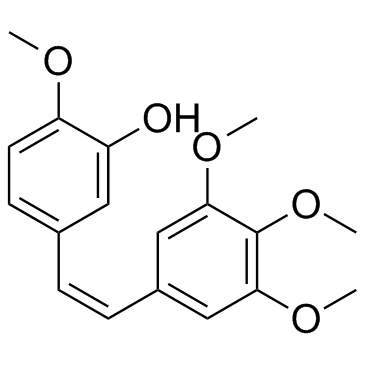 |
Combretastatin A4
CAS:117048-59-6 |
|
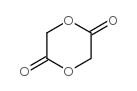 |
1,4-Dioxane-2,5-dione
CAS:502-97-6 |
|
 |
Colfosceril palmitate
CAS:63-89-8 |
|
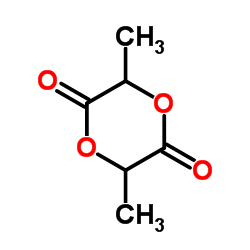 |
lactide
CAS:95-96-5 |
|
 |
DL-Alanine
CAS:302-72-7 |
|
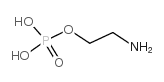 |
O-Phosphorylethanolamine
CAS:1071-23-4 |