| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
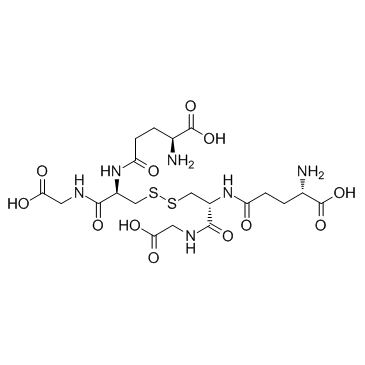 |
L(-)-Glutathione
CAS:27025-41-8 |
|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
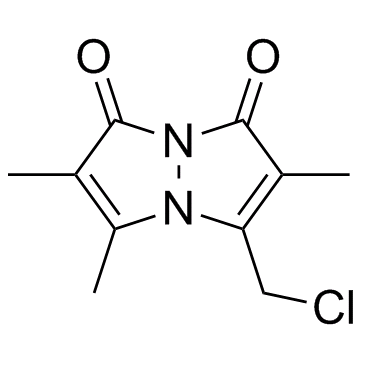 |
Monochlorobimane
CAS:76421-73-3 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
 |
L-Glutathione oxidized disodium salt
CAS:103239-24-3 |
|
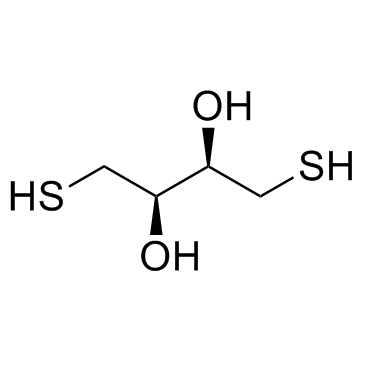 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
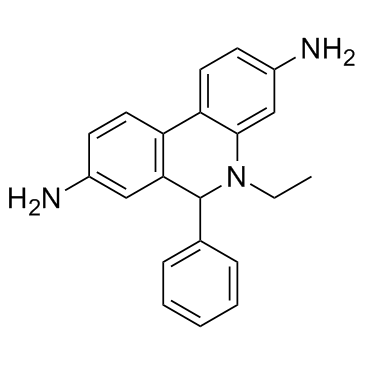 |
Dihydroethidium
CAS:104821-25-2 |
|
 |
2-Phenylindole
CAS:948-65-2 |