| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
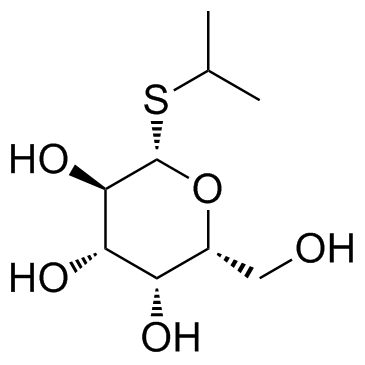 |
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside
CAS:367-93-1 |
|
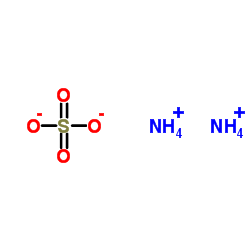 |
ammonium sulphate
CAS:7783-20-2 |
|
 |
DL-Lysine
CAS:70-54-2 |
|
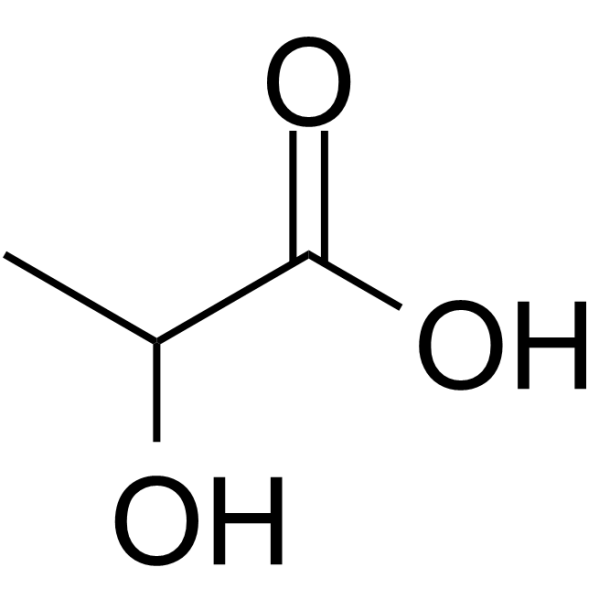 |
Lactic acid
CAS:50-21-5 |
|
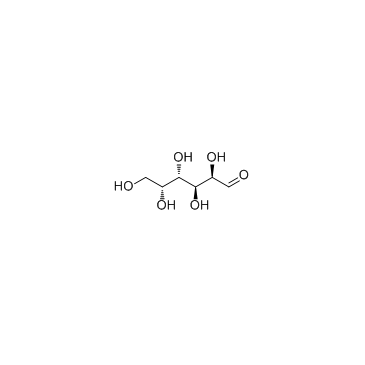 |
D-Galactose
CAS:59-23-4 |
|
 |
Uracil
CAS:66-22-8 |
|
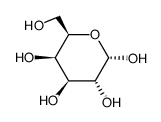 |
galactose
CAS:3646-73-9 |
|
 |
Maltose
CAS:69-79-4 |