Cromakalim
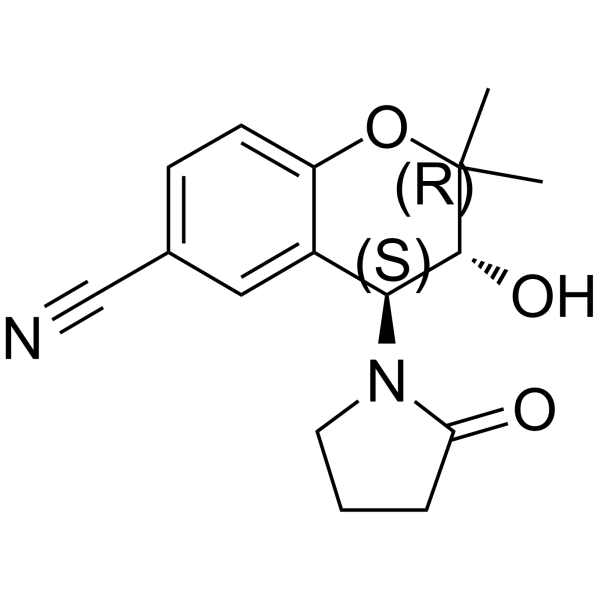
Cromakalim structure
|
Common Name | Cromakalim | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94470-67-4 | Molecular Weight | 286.33 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 482.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H20N2O3S | Melting Point | 242-244ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 245.5±28.7 °C | |
|
The relaxant action of nicorandil in bovine tracheal smooth muscle.
Pharmacology 89(5-6) , 327-32, (2012) The relaxant mechanisms of nicorandil were examined by comparing its effects with those of sodium nitroprusside and cromakalim in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. In preparations contracted with methacholine (0.3 μ mol/l) or high K(+)(40 mmol/l), nicorandil and... |
|
|
CYP-epoxygenases contribute to A2A receptor-mediated aortic relaxation via sarcolemmal KATP channels.
Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 303(10) , R1003-10, (2012) Previously, we have shown that A(2A) adenosine receptor (A(2A)AR) mediates aortic relaxation via cytochrome P-450 (CYP)-epoxygenases. However, the signaling mechanism is not understood properly. We hypothesized that ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(ATP)) channels play a... |
|
|
Phasic activity of urinary bladder smooth muscle in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat: effect of potassium channel modulators.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 660(2-3) , 431-7, (2011) Increased phasic activity in the bladder smooth muscle of animal models and patients with detrusor overactivity has been suggested to underlie the pathophysiology of overactive bladder. Potassium (K+) channels are key regulators of bladder smooth muscle tone ... |
|
|
Mineralocorticoids participate in the reduced vascular reactivity of pregnant rats.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 302(5) , H1195-201, (2012) The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system is markedly activated in pregnancy. We evaluated if mineralocorticoid receptors (MR), a major component of the RAA system, are involved in the reduced vascular reactivity associated with pregnancy. Canrenoate (MR... |
|
|
CaMKII inhibition hyperpolarizes membrane and blocks nitrergic IJP by closing a Cl(-) conductance in intestinal smooth muscle.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 303(2) , G240-6, (2012) The ionic basis of nitrergic "slow'" inhibitory junction potential (sIJP) is not fully understood. The purpose of the present study was to determine the nature and the role of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)-dependent ion conductance in nitrer... |
|
|
Role of potassium channels in the antidepressant-like effect of folic acid in the forced swimming test in mice.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 101(1) , 148-54, (2012) Potassium (K(+)) channels have been implicated in depressive disorders and in the mechanism of action of antidepressants. Considering that several studies have indicated that folic acid plays an important role in the pathophysiology of depression, the present... |
|
|
Humoral and cellular effects of the K(+)-channel activator cromakalim in man.
Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 37 , 609, (1989) The effect of cromakalim, a K(+)-channel activator, on the plasma renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, catecholamines and alpha-atrial natriuretic peptide, and on the intraerythrocyte concentration and transmembrane fluxes of Na+ and K+ has been investigated... |
|
|
Effects of cromakalim, pinacidil and nicorandil on cardiac refractoriness and arterial pressure in open-chest dogs.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 179 , 243, (1990) The cardiac electrophysiologic effects of the potassium channel activators cromakalim, pinacidil and nicorandil were determined in anesthetized open-chest normotensive dogs using conventional surface electrogram recording techniques. Intravenous administratio... |
|
|
Recent developments in the chemistry of potassium channel activators: the cromakalim analogs.
Curr. Med. Chem. 11(9) , 1213-22, (2004) Potassium channels play a crucial role in controlling the cell membrane potential. Among the different varieties of K(+) channels, the ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K(ATP) channels) have been characterized in numerous cell types, such as skeletal and smoo... |
|
|
Eicosapentaenoic acid reduces ischemic ventricular fibrillation via altering monophasic action potential in pigs.
J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 51(3) , 329-36, (2011) Although high intake of n-3 fatty acids is associated with reduced mortality of patients with ischemic heart disease, especially reduction in sudden cardiac death (SCD), the detailed mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Thus, the present study was designed to ... |