sodium arsenite
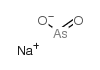
sodium arsenite structure
|
Common Name | sodium arsenite | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7784-46-5 | Molecular Weight | 130.91800 | |
| Density | 5.727 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 613 °C(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | AsHNaO2 | Melting Point | 817 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
p38 MAP kinase mediates arsenite-induced apoptosis through FOXO3a activation and induction of Bim transcription.
Apoptosis 13(6) , 803-10, (2008) Sodium arsenite induces apoptosis in PC12 cells by activating the stress-activated p38 MAP kinase and the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family protein Bim(EL). However, the relationship between p38 and Bim(EL) in this apoptosis has not been fully defined. Here, we repo... |
|
|
Embryonic exposure to sodium arsenite perturbs vascular development in zebrafish.
Aquat. Toxicol. 152 , 152-63, (2014) Exposure to arsenic in its inorganic form, arsenite, causes adverse effects to many different organs and tissues. Here, we have investigated arsenite-induced adverse effects on vascular tissues in the model organism zebrafish, Danio rerio. Zebrafish embryos w... |
|
|
Serine residue 115 of MAPK-activated protein kinase MK5 is crucial for its PKA-regulated nuclear export and biological function.
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68 , 847-62, (2011) The mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase-5 (MK5) resides predominantly in the nucleus of resting cells, but p38(MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinases-3 and -4 (ERK3 and ERK4), and protein kinase A (PKA) induce nucleocytoplasmic re... |
|
|
Microfluidic enrichment for the single cell analysis of circulating tumor cells.
Sci. Rep. 6 , 22076, (2016) Resistance to drug therapy is a major concern in cancer treatment. To probe clones resistant to chemotherapy, the current approach is to conduct pooled cell analysis. However, this can yield false negative outcomes, especially when we are analyzing a rare num... |
|
|
Missense mutation in the second RNA binding domain reveals a role for Prkra (PACT/RAX) during skull development.
PLoS ONE 6(12) , e28537, (2011) Random chemical mutagenesis of the mouse genome can causally connect genes to specific phenotypes. Using this approach, reduced pinna (rep) or microtia, a defect in ear development, was mapped to a small region of mouse chromosome 2. Sequencing of this region... |
|
|
Comparative functional genomic analysis identifies distinct and overlapping sets of genes required for resistance to monomethylarsonous acid (MMAIII) and arsenite (AsIII) in yeast.
Toxicol. Sci. 111(2) , 424-36, (2009) Arsenic is a human toxin and carcinogen commonly found as a contaminant in drinking water. Arsenite (As(III)) is the most toxic inorganic form, but recent evidence indicates that the metabolite monomethylarsonous acid (MMA(III)) is even more toxic. We have us... |
|
|
V-PROLI/NO, a nitric oxide donor prodrug, protects liver cells from arsenic-induced toxicity.
Cancer Sci. 100(3) , 382-8, (2009) Inorganic arsenic shows great promise in human cancer chemotherapy, although hepatotoxicity is a major limiting side-effect. O(2)-Vinyl 1-[2-(Carboxylato)pyrrolidin-1-yl]diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate (V-PROLI/NO) [Correction added after publication 19 December 200... |