Naloxone
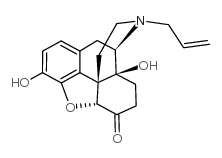
Naloxone structure
|
Common Name | Naloxone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 465-65-6 | Molecular Weight | 327.37 | |
| Density | 1.43 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 532.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H21NO4 | Melting Point | 184ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 276.1ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Morphine-induced internalization of the L83I mutant of the rat μ-opioid receptor.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(2) , 593-605, (2014) Naturally occurring single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within GPCRs can result in alterations in various pharmacological parameters. Understanding the regulation and function of endocytic trafficking of the μ-opioid receptor (MOP receptor) is of great imp... |
|
|
Sympathetic activity induced by naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal is blocked in genetically engineered mice lacking functional CRF1 receptor.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 283(1) , 42-9, (2015) There is large body evidence indicating that stress can lead to cardiovascular disease. However, the exact brain areas and the mechanisms involved remain to be revealed. Here, we performed a series of experiments to characterize the role of CRF1 receptor (CRF... |
|
|
Involvement of neurotransmitters in the action of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide-receptor system on passive avoidance learning in rats.
Neurochem. Res. 39(8) , 1477-83, (2014) The nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) receptor and its endogenous ligand plays role in several physiologic functions of the central nervous system, including pain, locomotion, anxiety and depression, reward and drug addiction, learning and memory. Previous... |
|
|
Relationship between noradrenaline release in the locus coeruleus and antiallodynic efficacy of analgesics in rats with painful diabetic neuropathy.
Life Sci. 92(23) , 1138-44, (2013) In animal models of neuropathic pain, the noradrenergic descending pain inhibitory pathways from the locus coeruleus (LC) may be suppressed. However, no study has investigated the correlation between noradrenaline (NA) release in the LC and efficacy of analge... |
|
|
μ-Opioid receptor activation and noradrenaline transport inhibition by tapentadol in rat single locus coeruleus neurons.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(2) , 460-8, (2014) Tapentadol is a novel analgesic that combines moderate μ-opioid receptor agonism and noradrenaline reuptake inhibition in a single molecule. Both mechanisms of action are involved in producing analgesia; however, the potency and efficacy of tapentadol in indi... |
|
|
Characteristics of scratching behavior in ADJM mice (atopic dermatitis from Japanese mice).
Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 37(2) , 202-6, (2015) In order to elucidate the characteristics of scratching behavior in atopic dermatitis from Japanese mice (ADJM) mice, the effects of some antagonists of pruritogens on this behavior were studied. Both male and female ADJM mice showed frequent scratching behav... |
|
|
Modeling nociception in zebrafish: a way forward for unbiased analgesic discovery.
PLoS ONE 10(1) , e0116766, (2015) Acute and chronic pain conditions are often debilitating, inflicting severe physiological, emotional and economic costs and affect a large percentage of the global population. However, the development of therapeutic analgesic agents based primarily on targete... |
|
|
Opioid receptor-dependent sex differences in synaptic plasticity in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway of the adult rat.
J. Neurosci. 35(4) , 1723-38, (2015) The mossy fiber (MF) pathway is critical to hippocampal function and influenced by gonadal hormones. Physiological data are limited, so we asked whether basal transmission and long-term potentiation (LTP) differed in slices of adult male and female rats. The ... |
|
|
Endogenous cholinergic neurotransmission contributes to behavioral sensitization to morphine.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0117601, (2015) Neuroplasticity in the mesolimbic dopaminergic system is critical for behavioral adaptations associated with opioid reward and addiction. These processes may be influenced by cholinergic transmission arising from the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDTg), a m... |
|
|
Opioid-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in rat enteric neurons following chronic morphine treatment.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e110230, (2014) Opioids, acting at μ opioid receptors, are commonly used for pain management. Chronic opioid treatment induces cellular adaptations, which trigger long-term side effects, including constipation mediated by enteric neurons. We tested the hypothesis that chroni... |