Ethoxzolamide
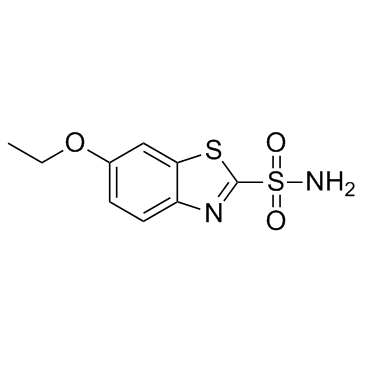
Ethoxzolamide structure
|
Common Name | Ethoxzolamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 452-35-7 | Molecular Weight | 258.31700 | |
| Density | 1.47g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 464.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10N2O3S2 | Melting Point | 190-193ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 235ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Transport activity of the sodium bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 is enhanced by different isoforms of carbonic anhydrase.
PLoS ONE 6(11) , e27167, (2011) Transport metabolons have been discussed between carbonic anhydrase II (CAII) and several membrane transporters. We have now studied different CA isoforms, expressed in Xenopus oocytes alone and together with the electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter ... |
|
|
Reversed electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 is the major acid loader during recovery from cytosolic alkalosis in mouse cortical astrocytes.
J. Physiol. 593 , 3533-47, (2015) The regulation of H(+) i from cytosolic alkalosis has generally been attributed to the activity of Cl(-) -coupled acid loaders/base extruders in most cell types, including brain cells. The present study demonstrates that outwardly-directed sodium bicarbonate ... |
|
|
Functional interaction between bicarbonate transporters and carbonic anhydrase modulates lactate uptake into mouse cardiomyocytes.
Pflugers Arch. 467 , 1469-80, (2015) Blood-derived lactate is a precious energy substrate for the heart muscle. Lactate is transported into cardiomyocytes via monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) together with H(+), which couples lactate uptake to cellular pH regulation. In this study, we have in... |
|
|
High effective cytosolic H+ buffering in mouse cortical astrocytes attributable to fast bicarbonate transport.
Glia 63 , 1581-94, (2015) Cytosolic H(+) buffering plays a major role for shaping intracellular H(+) shifts and hence for the availability of H(+) for biochemical reactions and acid/base-coupled transport processes. H(+) buffering is one of the prime means to protect the cell from lar... |
|
|
Development and validation of an UPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of ethoxzolamide in blood, brain tissue, and bioequivalent buffers: applications to absorption, brain distribution, and pharmacokinetic studies.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 986-987 , 54-9, (2015) The purpose of this study is to develop and validate an UPLC-MS/MS method to quantify ethoxzolamide in plasma (EZ) and apply the method to absorption, brain distribution, as well as pharmacokinetic studies. A C₁₈ column was used with 0.1% of formic acid in ac... |
|
|
Carbonic anhydrase activation is associated with worsened pathological remodeling in human ischemic diabetic cardiomyopathy.
J. Am. Heart Assoc. 3(2) , e000434, (2014) Diabetes mellitus (DM) has multifactorial detrimental effects on myocardial tissue. Recently, carbonic anhydrases (CAs) have been shown to play a major role in diabetic microangiopathy but their role in the diabetic cardiomyopathy is still unknown.We obtained... |
|
|
Hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX facilitates lactate flux in human breast cancer cells by non-catalytic function.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13605, (2015) The most aggressive tumour cells, which often reside in hypoxic environments, rely on glycolysis for energy production. Thereby they release vast amounts of lactate and protons via monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs), which exacerbates extracellular acidifica... |
|
|
Mechanisms of transepithelial ammonia excretion and luminal alkalinization in the gut of an intestinal air-breathing fish, Misgurnus anguilliacaudatus.
J. Exp. Biol. 216(Pt 4) , 623-32, (2013) The weatherloach, Misgurnus angulliacaudatus, is an intestinal air-breathing, freshwater fish that has the unique ability to excrete ammonia through gut volatilization when branchial and cutaneous routes are compromised during high environmental ammonia or ai... |
|
|
Nonenzymatic augmentation of lactate transport via monocarboxylate transporter isoform 4 by carbonic anhydrase II.
J. Membr. Biol. 234 , 125-35, (2010) Monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) are carriers of high-energy metabolites like lactate and pyruvate, and different MCT isoforms are expressed in a wide range of cells and tissues. Transport activity of MCT isoform 1 (MCT1), heterologously expressed in Xenop... |
|
|
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: the X-ray crystal structure of ethoxzolamide complexed to human isoform II reveals the importance of thr200 and gln92 for obtaining tight-binding inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18(8) , 2669-74, (2008) Ethoxzolamide, an almost forgotten inhibitor of the metalloenzyme carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1), is the only classical inhibitor whose structure in adduct with any isoform was not reported yet. We report here the inhibition data of this molecule with th... |