1,1,2-Trichlorotrifluoroethane
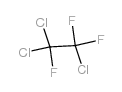
1,1,2-Trichlorotrifluoroethane structure
|
Common Name | 1,1,2-Trichlorotrifluoroethane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 76-13-1 | Molecular Weight | 187.37600 | |
| Density | 1.57 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 47-48 °C(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | C2Cl3F3 | Melting Point | −35 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | 195°C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Rotavirus increases levels of lipidated LC3 supporting accumulation of infectious progeny virus without inducing autophagosome formation.
PLoS ONE 9(4) , e95197, (2014) Replication of many RNA viruses benefits from subversion of the autophagic pathway through many different mechanisms. Rotavirus, the main etiologic agent of pediatric gastroenteritis worldwide, has been recently described to induce accumulation of autophagoso... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of CFC-11, CFC-12 and CFC-113 in seawater samples using a purge and trap gas-chromatographic system
Talanta 80(2) , 959-66, (2009) We have optimized the analytical parameters of a homemade instrument for the simultaneous measurement of the chlorofluorocarbons CCl 2F 2 (CFC-12), CCl 3F (CFC-11) and C 2Cl 3F 3 (CFC-113) in seawater. Seawater samples are flame sealed into 60 ml glass ampoul... |
|
|
Atrial fibrillation and sudden death related to occupational solvent exposure.
Am. J. Ind. Med. 25(5) , 731-5, (1994) Two cases of atrial fibrillation and one case of sudden death occurred in workers exposed to trifluorotrichloroethane (CFC 113) as a solvent/degreasing agent. This agent and related halogenated hydrocarbons are widely used in industry as solvents and degreasi... |
|
|
Raised concentration of serum bile acids following occupational exposure to halogenated solvents, 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane and trichloroethylene.
Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 70(3) , 187-94, (1997) The objectives of this study were threefold. First, to examine the hepatic effects of occupational exposure to 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane (FC 113) using conventional and newer tests (serum bile acids) of hepatobiliary function. Second, to assess th... |
|
|
Analysis of virus-specific RNA species and proteins in Freon-113 preparations of the Borna disease virus.
Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 182(5) , 271-80, (1993) Treatment of homogenates from Borna disease virus (BDV)-infected brain tissue or cell cultures with Freon-113 yielded infectious particles with a buoyant density of 1.16-1.22 g/ml. Positive- and negative-stranded BDV-specific RNA species as well as three viru... |
|
|
Enhanced arrhythmogenicity of Freon 113 by hypoxia in the perfused rat heart.
Toxicol. Ind. Health 6(3-4) , 493-8, (1990) The interaction of Freon 113 (1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane) and hypoxia on the heart conduction system was studied using electrocardiogram monitoring of isolated perfused rat hearts. Freon 113 (0.2 mM) alone elicited significant atrioventricular cond... |
|
|
Secondary arterial hypertension linked to Freon exposure.
South. Med. J. 89(5) , 516-8, (1996) Freons are generally considered to be minimally toxic. There are no reports in the literature of Freons causing secondary arterial hypertension. We report two cases of acute, massive Freon exposure that preceded secondary arterial hypertension. We hypothesize... |
|
|
Possible aircrew intoxication caused by accidental release of RainBoe: a case report.
Aviat. Space. Environ. Med. 68(12) , 1159-60, (1997)
|
|
|
Transport of hydrocarbons from an emplaced fuel source experiment in the vadose zone at Airbase Vaerløse, Denmark.
J. Contam. Hydrol. 81(1-4) , 1-33, (2005) An emplaced hydrocarbon source field experiment was conducted in the relatively homogeneous sandy geology of the vadose zone at Airbase Vaerløse, Denmark. The source (10.2 l of NAPL) consisted of 13 hydrocarbons (n-, iso- and cyclo-alkanes and aromates) and C... |
|
|
[An industrial accidental death due to Freon 113 poisoning. Toxicological analysis of its cause of death].
Nihon Hoigaku. Zasshi 37(4) , 428-33, (1983)
|