Ammonium bisulfate
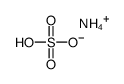
Ammonium bisulfate structure
|
Common Name | Ammonium bisulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7803-63-6 | Molecular Weight | 115.10900 | |
| Density | 1.79 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 350 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | H5NO4S | Melting Point | 147 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Potential risks to human respiratory health from "acid fog": evidence from experimental studies of volunteers.
Environ. Health Perspect. 63 , 57-61, (1985) Observations of high acidity (pH as low as 1.7) in fogwater collected in polluted areas have provoked concern for public health. Effects of exposure to acidic pollutants have not been studied under foggy conditions; thus there is no directly relevant informat... |
|
|
Source apportionment of fine particulate matter in the southeastern United States.
J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 57(9) , 1123-35, (2007) Particulate matter (PM) less than 2.5 microm in size (PM2.5) source apportionment by chemical mass balance receptor modeling was performed to enhance regional characterization of source impacts in the southeastern United States. Secondary particles, such as N... |
|
|
Pulmonary effects of ultrafine and fine ammonium salts aerosols in healthy and monocrotaline-treated rats following short-term exposure.
Inhal. Toxicol. 14(12) , 1215-29, (2002) In the present study the effects of a 3-day inhalation exposure to model compounds for ambient particulate matter were investigated: ammonium bisulfate, ammonium ferrosulfate, and ammonium nitrate, all components of the secondary aerosol fraction of ambient p... |
|
|
Toxicity of chemical components of fine particles inhaled by aged rats: effects of concentration.
J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 53(9) , 1080-7, (2003) This study tested the hypothesis that exposure to mixtures containing fine particles and ozone (O3) would cause pulmonary injury and decrements in functions of immunological cells in exposed rats (22-24 months old) in a dose-dependent manner. Rats were expose... |
|
|
Ammonium bisulfite contact dermatitis: face eczema due to a bleaching ointment used during hair-dying.
Contact Dermatitis 55(2) , 124, (2006)
|
|
|
Heterogeneous reactions of alkylamines with ammonium sulfate and ammonium bisulfate.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 45 , 4748-4755, (2011) The heterogeneous reactions between alkylamines and ammonium salts (ammonium sulfate and ammonium bisulfate) have been studied using a low-pressure fast flow reactor coupled to an ion drift-chemical ionization mass spectrometer (ID-CIMS) at 293 ± 2 K. The upt... |
|
|
Size-dependent reactions of ammonium bisulfate clusters with dimethylamine.
J. Phys. Chem. A 114 , 11638-11644, (2010) The reaction kinetics of ammonium bisulfate clusters with dimethylamine (DMA) gas were investigated using Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FTICR-MS). Clusters ranged in size from 1 to 10 bisulfate ions. Although displacement of the... |
|
|
Temporal Dynamics of Active Prokaryotic Nitrifiers and Archaeal Communities from River to Sea.
Microb. Ecol. 70 , 473-83, (2015) To test if different niches for potential nitrifiers exist in estuarine systems, we assessed by pyrosequencing the diversity of archaeal gene transcript markers for taxonomy (16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA)) during an entire year along a salinity gradient in surface... |
|
|
Combination of apolipoprotein A1-modi liposome-doxorubicin with autophagy inhibitors overcame drug resistance in vitro.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(12) , 3994-4004, (2014) Multidrug resistance (MDR) represents the major drawback in chemotherapy. Liposome-based approaches could reverse MDR to some extent through circumventing the active efflux effect of P-glycoprotein. However, the reverse power of liposome is very limited becau... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of a novel ammonium overly sensitive mutant, amos2, in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Planta 235(2) , 239-52, (2012) Ammonium (NH(4)(+)) toxicity is a significant agricultural problem globally, compromising crop growth and productivity in many areas. However, the molecular mechanisms of NH(4)(+) toxicity are still poorly understood, in part due to a lack of valuable genetic... |