Calcium Propionate
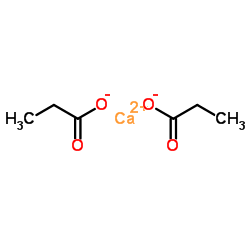
Calcium Propionate structure
|
Common Name | Calcium Propionate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4075-81-4 | Molecular Weight | 186.219 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 141.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10CaO4 | Melting Point | 300 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 57.7ºC | |
|
Development of a model describing the inhibitory effect of selected preservatives on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes in a meat model system.
Food Microbiol. 53 , 115-21, (2015) The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of seven independent factors consisting of sodium nitrite, pH, sodium chloride, sodium acetate, sodium lactate syrup, calcium propionate and a blend of nisin and hop alpha acids on the growth rate of List... |
|
|
Optimization of low-temperature blanching combined with calcium treatment to inactivate Escherichia coli O157:H7 on fresh-cut spinach.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 119 , 139-48, (2015) To develop a mild blanching method with calcium salts to ensure microbiological safety and quality of fresh-cut spinach.The antimicrobial efficacy of eight calcium salts was evaluated on Escherichia coli O157:H7 at 45-65°C and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2 ) sho... |
|
|
The effect of sourdough and calcium propionate on the microbial shelf-life of salt reduced bread.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 96(2) , 493-501, (2012) The consumption of low-salt bread represents an efficient way to improve public health by decreasing cardiovascular health issues related to increased intakes of sodium chloride (NaCl). The reduction of NaCl influences the bread quality characteristics, in pa... |
|
|
DNA damage in human lymphocytes exposed to four food additives in vitro.
Toxicol. Ind. Health , (2012) In vitro genotoxic effects of antioxidant additives, such as citric acid (CA) and phosphoric acid (PA) and their combination, as well as antimicrobial additives, such as benzoic acid (BA) and calcium propionate (CP), on human lymphocytes were determined using... |
|
|
Effects of calcium salts on growth, polygalacturonase activity, and infection of peach fruit by Monilinia fructicola. Biggs AR, et al.
Plant Dis. 81(4) , 399-407, (1997)
|