Atractylenolide I
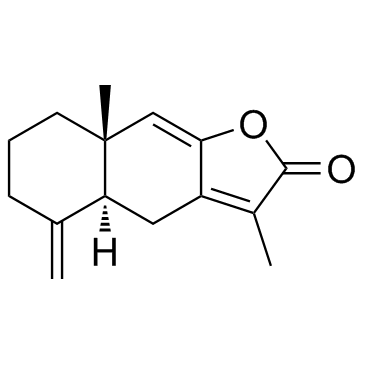
Atractylenolide I structure
|
Common Name | Atractylenolide I | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73069-13-3 | Molecular Weight | 230.302 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 405.0±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H18O2 | Melting Point | 121-123 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 170.8±25.9 °C | |
|
GABA(A) receptor modulators from Chinese herbal medicines traditionally applied against insomnia and anxiety.
Phytomedicine 19 , 334-340, (2012) Several Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs) are used in the treatment of insomnia, restlessness, or anxiety. However, mechanisms underlying this effect and scientific proof for their traditional use is scarce. In the present study CHMs were screened for their abi... |
|
|
Quantitative analysis of atractylenolide I in rat plasma by LC–MS/MS method and its application to pharmacokinetic study
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 58 , 172-176, (2012) Highlights ► We develop an HPLC/MS method for quantification of atractylenolide I in rat plasma. ► Pharmacokinetics was performed in rats ingested with 20 g/kg Atractylodis extract. ► Atractylenolide I was found to be absorbed quickly within 1 h. ► The biolog... |
|
|
Screening for compounds with aromatase inhibiting activities from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.
Molecules 16 , 3146-3151, (2011) Ten compounds were isolated from the dichloromethane extract of Atractylodes macrocephala and their aromatase inhibiting activities were tested using an in vitro fluorescent-based aromatase assay. The results indicated that atractylenolide I, atractylenolide ... |
|
|
Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 by the root extract of Cyathula officinalis Kuan and its constituents in IL-1β-treated chondrocytes.
Planta Med. 77 , 1528-1530, (2011) The roots of Cyathula officinalis Kuan are widely used in Chinese medicine for the treatment of inflammatory disorders. Here, the ability of C. officinalis Kuan to downregulate matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 was examined since MMP-13 is an important enzyme... |
|
|
Atractylenolide-I sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel by blocking activation of TLR4/MyD88-dependent pathway.
Sci. Rep. 4 , 3840, (2014) Paclitaxel, a known TLR4 ligand, leads to activation of TLR4/MyD88-dependent pathway that mediates chemoresistance and tumor progression in epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC). Atractylenolide-I (AO-I), a novel TLR4-antagonizing agent, inhibits TLR4 signaling ... |