4-Toluenesulfonamide
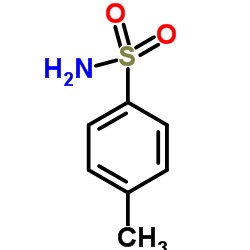
4-Toluenesulfonamide structure
|
Common Name | 4-Toluenesulfonamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 70-55-3 | Molecular Weight | 171.22 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 322.2±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9NO2S | Melting Point | 134-137 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 148.6±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition studies with anions and sulfonamides of a new cytosolic enzyme from the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 710-4, (2011) The catalytic activity and the inhibition of a new coral carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1), from the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata, STPCA-2, has been investigated. STPCA-2 has high catalytic activity for the physiological reaction being less sen... |
|
|
Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a fragment-based approach.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 591-602, (2011) Fragment-based lead design (FBLD) has been used to identify new metal-binding groups for metalloenzyme inhibitors. When screened at 1 mM, a chelator fragment library (CFL-1.1) of 96 compounds produced hit rates ranging from 29% to 43% for five matrix metallop... |
|
|
Cloning, characterization and sulfonamide inhibition studies of an α-carbonic anhydrase from the living fossil sponge Astrosclera willeyana.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20 , 1403-10, (2012) The α-carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1) Astrosclerin-3 previously isolated from the living fossil sponge Astrosclera willeyana (Jackson et al., Science 2007, 316, 1893), was cloned, kinetically characterized and investigated for its inhibition properties wi... |
|
|
Inhibition studies of the β-carbonic anhydrases from the bacterial pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium with sulfonamides and sulfamates.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 5023-30, (2011) The two β-carbonic anhydrases (CAs, EC 4.2.1.1) from the bacterial pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, stCA 1 and stCA 2, were investigated for their inhibition with a large panel of sulfonamides and sulfamates. Unlike inorganic anions, which ar... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of benzothiazoles, benzotriazoles and benzosulfonamides by solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry in environmental aqueous matrices and human urine
J. Chromatogr. A. 1338 , 164-73, (2014) • Benzothiazoles, benzotriazoles and benzosulfonamides determination in aqueous matrices. • New environmental-friendly and high-throughput protocol developed by SPME-GC-QqQMS. • Sample preparation strategy completely avoids the use of organic solvents. • MRM ... |
|
|
The allergens of nail polish. (I). Allergenic constituents of common nail polish and toluenesulfonamide-formaldehyde resin (TS-F-R).
Contact Dermatitis 33(3) , 157-64, (1995) Nail polish that has completely dried on the fingernails contains water-soluble components that attain the skin during extensive but transient contact. This was proven by water extraction of thin layers of nail polish that had been painted onto glass plates a... |
|
|
Behaviour and biodegradation of sulfonamides (p-TSA, o-TSA, BSA) during drinking water treatment.
Chemosphere 71(8) , 1574-81, (2008) Three sulfonamides -para-toluenesulfonamide (p-TSA), ortho-toluenesulfonamide (o-TSA) and benzenesulfonamide (BSA) - have recently been detected in groundwater within a catchment area of one drinking water treatment plant (DWTP), which is located downstream o... |
|
|
Molecular structure and conformations of para-methylbenzene sulfonamide and ortho-methylbenzene sulfonamide: gas electron diffraction and quantum chemical calculations study.
J. Phys. Chem. A 112(13) , 2969-76, (2008) The molecular structure and conformational properties of para-methylbenzene sulfonamide (4-MBSA) and ortho-methylbenzene sulfonamide (2-MBSA) have been studied by gas electron diffraction (GED) and quantum chemical methods (B3LYP/6-311+G** and MP2/6-31G**). Q... |
|
|
Cloning, characterization, and inhibition studies of a beta-carbonic anhydrase from Brucella suis.
J. Med. Chem. 53 , 2277-85, (2010) A beta-carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1) from the bacterial pathogen Brucella suis, bsCA 1, has been cloned, purified, and characterized kinetically. bsCA 1 has appreciable activity as catalyst for the hydration of CO(2) to bicarbonate, with a k(cat) of 6.4... |
|
|
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Characterization and inhibition studies of the most active beta-carbonic anhydrase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Rv3588c.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 6649-54, (2009) The Rv3588c gene product of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a beta-carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1) denominated here mtCA 2, shows the highest catalytic activity for CO(2) hydration (k(cat) of 9.8 x 10(5)s(-1), and k(cat)/K(m) of 9.3 x 10(7)M(-1)s(-1)) among t... |