4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate
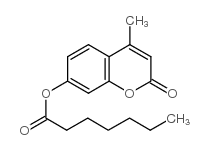
4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate structure
|
Common Name | 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 18319-92-1 | Molecular Weight | 288.33800 | |
| Density | 1.129g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 429ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H20O4 | Melting Point | 41-42 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 214.5ºC | |
|
Concurrent MEK and autophagy inhibition is required to restore cell death associated danger-signalling in Vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 93(3) , 290-304, (2015) Vemurafenib (PLX4032), an inhibitor of BRAF(V600E), has demonstrated significant clinical anti-melanoma effects. However, the majority of treated patients develop resistance, due to a variety of molecular mechanisms including MAPK reactivation through MEK. Th... |
|
|
A lipid switch unlocks Parkinson's disease-associated ATP13A2.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , 9040-5, (2015) ATP13A2 is a lysosomal P-type transport ATPase that has been implicated in Kufor-Rakeb syndrome and Parkinson's disease (PD), providing protection against α-synuclein, Mn(2+), and Zn(2+) toxicity in various model systems. So far, the molecular function and re... |
|
|
Rapid detection of total and fecal coliforms in water by enzymatic hydrolysis of 4-methylumbelliferone-beta-D-galactoside.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54(8) , 2118-22, (1988) Three fluorogenic methylumbelliferone (MU) substrates were evaluated for rapid detection of total and fecal coliform bacteria (TC and FC) in drinking water. 4-MU-beta-D-galactoside, MU-heptanoate, and MU-glucuronide were used to determine enzyme activity as a... |
|
|
A fluorometric rapid microassay to identify anti-proliferative compounds for human melanoma cells in vitro.
Melanoma Res. 1(2) , 91-5, (1991) A simple, rapid and reproducible assay for the determination of melanoma cell proliferation in vitro is described, based on the hydrolysis of a fluorogenic substrate by cell esterases in the cytoplasm of living cells. Human melanoma cells were cultured at sev... |
|
|
A rapid fluorometric assay for the determination of keratinocyte proliferation in vitro.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 93(4) , 532-4, (1989) In the present study we describe a simple technique for the determination of keratinocyte proliferation in vitro, based on the hydrolysis of a fluorogenic substrate by cell esterases. Normal and transformed human keratinocytes were grown in microtiter plates ... |
|
|
Mutation of F417 but not of L418 or L420 in the lipid binding domain decreases the activity of triacylglycerol hydrolase.
J. Lipid Res. 47(2) , 375-83, (2006) Human triacylglycerol hydrolase (hTGH) has been shown to play a role in hepatic lipid metabolism. Triacylglycerol hydrolase (TGH) hydrolyzes insoluble carboxylic esters at lipid/water interfaces, although the mechanism by which the enzyme adsorbs to lipid dro... |
|
|
A rapid and sensitive fluorometric microassay for determining cell mediated cytotoxicity to adherent growing cell lines.
J. Immunol. Methods 156(1) , 1-8, (1992) In order to measure cell mediated cytotoxicity to adherent growing cell lines in vitro more rapidly and conveniently, a fluorometric microassay was developed and results were compared with those obtained by the 51Cr release assay. The fluorometric method is b... |
|
|
Production of 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate hydrolase by Escherichia coli exposed to seawater.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55(9) , 2424-7, (1989) The production of an enzyme, 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate hydrolase, in Escherichia coli exposed to enriched and nonenriched seawater was studied. In all media, except for seawater with no or very small amounts of organic material and seawater enriched wit... |
|
|
A simple, rapid and sensitive fluorimetric assay for the measurement of cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
J. Immunol. Methods 185(2) , 199-208, (1995) A fluorimetric method using 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate (MUH) has been developed for detecting cell-mediated cytotoxicity and cell proliferation. The assay is based on the hydrolysis of the fluorochrome (MUH) by intracellular esterases of viable cells res... |
|
|
A fluorometric assay for determining cell growth in lymphocyte proliferation and lymphokine assays.
J. Immunol. Methods 105(1) , 55-62, (1987) A microplate method for assessing cell growth and viability based on the hydrolysis of fluorogenic substrates by cell esterases has been investigated. Living cells incubated with fluorescein diacetate or 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate generate a fluorescent ... |