Applied and Environmental Microbiology
1989-09-01
Production of 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate hydrolase by Escherichia coli exposed to seawater.
L Fiksdal, M Pommepuy, A Derrien, M Cormier
Index: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55(9) , 2424-7, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The production of an enzyme, 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate hydrolase, in Escherichia coli exposed to enriched and nonenriched seawater was studied. In all media, except for seawater with no or very small amounts of organic material and seawater enriched with peptone, 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate hydrolase activity increased by 2 to 3 orders of magnitude within 2 days. Increased enzyme activity was assumed to be related to cells not undergoing lysis but adapting to conditions of nutrient limitation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
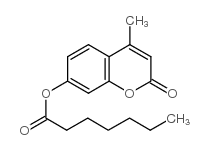 |
4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate
CAS:18319-92-1 |
C17H20O4 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Concurrent MEK and autophagy inhibition is required to resto...
2015-02-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 93(3) , 290-304, (2015)] |
|
A lipid switch unlocks Parkinson's disease-associated ATP13A...
2015-07-21 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , 9040-5, (2015)] |
|
Rapid detection of total and fecal coliforms in water by enz...
1988-08-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54(8) , 2118-22, (1988)] |
|
A fluorometric rapid microassay to identify anti-proliferati...
1991-01-01 [Melanoma Res. 1(2) , 91-5, (1991)] |
|
A rapid fluorometric assay for the determination of keratino...
1989-10-01 [J. Invest. Dermatol. 93(4) , 532-4, (1989)] |