Dipyridamole
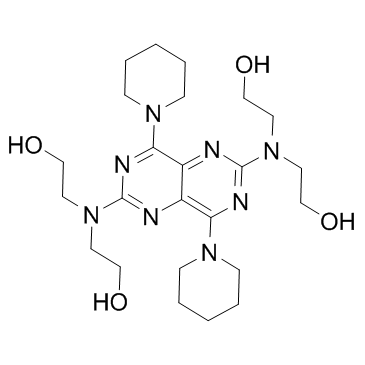
Dipyridamole structure
|
Common Name | Dipyridamole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58-32-2 | Molecular Weight | 504.626 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 806.5±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40N8O4 | Melting Point | 165-166ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 441.5±37.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Hypoxanthine uptake by skeletal muscle microvascular endothelial cells from equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1)-null mice: effect of oxidative stress.
Microvasc. Res. 98 , 16-22, (2015) Adenosine is an endogenous regulator of vascular tone. This activity of adenosine is terminated by its uptake and metabolism by microvascular endothelial cells (MVEC). The predominant transporter involved is ENT1 (equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype ... |
|
|
Oxidative stress modulates nucleobase transport in microvascular endothelial cells
Microvasc. Res. 95 , 68-75, (2014) Purine nucleosides and nucleobases play key roles in the physiological response to vascular ischemia/reperfusion events. The intra- and extracellular concentrations of these compounds are controlled, in part, by equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype 1 ... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Correlating FAAH and anandamide cellular uptake inhibition using N-alkylcarbamate inhibitors: from ultrapotent to hyperpotent.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 92(4) , 669-89, (2014) Besides the suggested role of a putative endocannabinoid membrane transporter mediating the cellular uptake of the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA), this process is intrinsically coupled to AEA degradation by the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Differentia... |
|
|
Detection of Infertility-related Neutralizing Antibodies with a Cell-free Microfluidic Method.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 16551, (2015) The unwanted emergence of neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) against an endogenous or a therapeutic protein can result in deficiency diseases or therapy failure. Here, we developed a cell-free microfluidic method for the sensitive detection and quantification of ... |
|
|
Prediction and identification of drug interactions with the human ATP-binding cassette transporter multidrug-resistance associated protein 2 (MRP2; ABCC2).
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 3275-87, (2008) The chemical space of registered oral drugs was explored for inhibitors of the human multidrug-resistance associated protein 2 (MRP2; ABCC2), using a data set of 191 structurally diverse drugs and drug-like compounds. The data set included a new reference set... |