reactive green 19
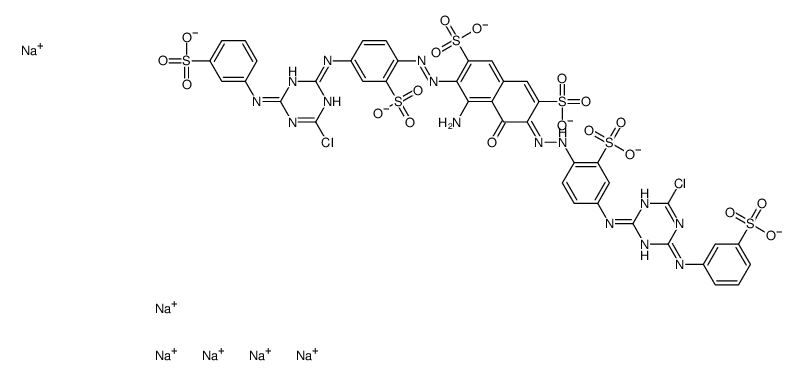
reactive green 19 structure
|
Common Name | reactive green 19 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 61931-49-5 | Molecular Weight | 1418.93000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H23Cl2N15Na6O19S6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Bioassay using a labeled oligonucleotide obtained by in vitro selection.
Biotechnol. Prog. 13(6) , 873-4, (1997) A new bioassay system using an oligodeoxyribonucleotide (DNA) obtained by the in vitro selection method is described. The DNA aptamer which selectively binds to a target molecule, Reactive Green 19 (RG19), was labeled with fluorescein. The circular dichroism ... |
|
|
Studies on an enzyme, S-formylglutathione hydrolase, of the dissimilatory pathway of methanol in Candida boidinii.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 614(1) , 81-91, (1980) In Candida boidinii, S-formylglutathione formed by reaction of the glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase is hydrolyzed to formate and glutathione by a special enzyme, S-formylglutathione hydrolase which is induced in C. boidinii along with the othe... |
|
|
Sesuvium portulacastrum (L.) L.: a potential halophyte for the degradation of toxic textile dye, Green HE4B.
Planta 235(5) , 1051-63, (2012) Sesuvium portulacastrum is a common halophyte growing well in adverse surroundings and is exploited mainly for the environmental protection including phytoremediation, desalination and stabilization of contaminated soil. In the present investigation, attempts... |
|
|
Rapid purification of two thermophilic proteinases using dye-ligand chromatography.
J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 32(1) , 1-6, (1996) Dye-ligand chromatography has been used successfully for the purification of extracellular thermostable proteinases from thermophilic Bacillus and Thermus cultures. Single-step purification factors of up to 115-fold (for Thermus protease) and 2195-fold (for B... |
|
|
Random UV mutagenesis approach for enhanced biodegradation of sulfonated azo dye, Green HE4B.
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 169(5) , 1467-81, (2013) The objective of the study was to execute mutant bacteria for efficient biodegradation of sulfonated azo dye, Green HE4B (GHE4B). UV irradiation was used to introduce random mutations in Pseudomonas sp. LBC1. Genetic alterations induced by UV irradiation in s... |
|
|
Probing the substrate-binding sites of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases with the procion dye green HE-4BD.
Biochem. J. 258(3) , 715-21, (1989) A reactive bis-dichloro derivative of the Procion dye Green HE-4BD was shown to inactivate irreversibly methionyl-tRNA synthetase (MTS) from Escherichia coli and also tryptophyl-tRNA synthetase (WTS) and tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (YTS) from Bacillus stearotherm... |
|
|
Surface energy components of a dye-ligand immobilized pHEMA membranes: effects of their molecular attracting forces for non-covalent interactions with IgG and HSA in aqueous media.
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 37(5) , 249-56, (2005) In the present paper, we report the study of the adsorption behaviour of human immunoglobulin G (IgG), human serum albumin (HSA) and polyethylenimine (PEI) onto surfaces of Procion Green HE-4BD (PG) immobilized poly(hydroxyethylmethacrylate) (pHEMA) membranes... |