H-GABA-Ome.HCl
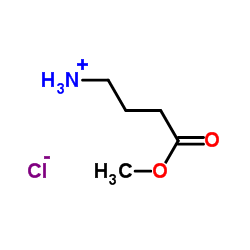
H-GABA-Ome.HCl structure
|
Common Name | H-GABA-Ome.HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13031-60-2 | Molecular Weight | 153.61 | |
| Density | 0.99g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 164.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H12ClNO2 | Melting Point | 120-125ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 38.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Tandem ring-opening decarboxylation of cyclopropane hemimalonates with sodium azide: a short route to γ-aminobutyric acid esters.
J. Org. Chem. 77(15) , 6634-7, (2012) Cyclopropane hemimalonates, when treated with sodium azide, undergo a tandem ring-opening decarboxylation to produce γ-azidobutyric acids in good yields. These adducts were hydrogenated to form γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) methyl esters. |
|
|
[Effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs on the brain GABA-ergic system participating in cardiovascular regulation].
Farmakol. Toksikol. 49(6) , 31-4, (1986) In pentobarbital-anesthetized cats GABA methylester (MEG) and beta-phenyl-GABA methylester (MEF) administered intravenously in doses of 1/100, 1/30, 1/10 of LD50 and injected intracerebroventricularly in doses of 0.1 and 0.5 mg produce hypotension, These effe... |
|
|
4-aminobutyric acid methyl ester hydrochloride, a precursor of 4-aminobutyric acid.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 32(6) , 1093-6, (1983) 4-Aminobutyric methyl ester hydrochloride (GME) is able to cross the blood-brain barrier after intracardiac administration to the rat. GME has an LD50 of 1300 mg/kg in mice and 950 mg/kg in rats, exhibits an antiaggressive effect and is able to decrease isoni... |