Glabridin
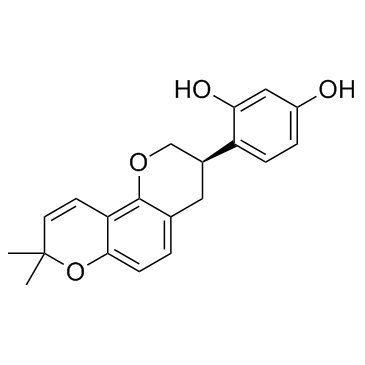
Glabridin structure
|
Common Name | Glabridin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59870-68-7 | Molecular Weight | 324.37 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 518.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H20O4 | Melting Point | 154-155ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 267.4±30.1 °C | |
|
Glabridin inhibits migration and invasion by transcriptional inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase 9 through modulation of NF-κB and AP-1 activity in human liver cancer cells.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 171(12) , 3037-50, (2014) High mortality and morbidity rates for hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan primarily result from uncontrolled tumour metastasis. Glabridin, a prenylated isoflavonoid of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) roots, is associated with a wide range of biological properti... |
|
|
Novel phytonutrient contributors to antioxidant protection against cardiovascular disease
Nutrition 28(6) , 605-10, (2012) The associations linking endothelial inflammation, endothelial oxidative stress, and atherogenesis and the potential for dietary phytonutrients to decrease the impact of these associations were assessed. A detailed literature review was conducted and summariz... |
|
|
Glabridin inhibits migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by inhibiting the FAK/rho signaling pathway.
Integr. Cancer Ther. 10(4) , 341-9, (2011) This study reports the antimigration, anti-invasive effect of glabridin, a flavonoid obtained from licorice, in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Glabridin exhibited effective inhibition of cell metastasis by decreasing cancer cell migration and in... |
|
|
Inhibition of bone marrow-derived dendritic cell maturation by glabridin.
Int. Immunopharmacol. 10(10) , 1185-93, (2010) Glabridin has multiple pharmacological activities including anti-microbial, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-nephritic, anti-inflammatory and cardiovascular protective activities. In this study, we investigated the effect of glabridin on dendritic cells, which play... |
|
|
Phytochemistry and biological properties of glabridin.
Fitoterapia 90 , 160-84, (2013) Glabridin, a prenylated isoflavonoid of G. glabra L. roots (European licorice, Fabaceae), has been associated with a wide range of biological properties such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-atherogenic, regulation of energy metabolism, estrogenic, neu... |
|
|
Antifungal activity of Glycyrrhiza glabra extracts and its active constituent glabridin.
Phytother Res. 23(8) , 1190-3, (2009) Glabridin, an active constituent of Glycyrrhiza glabra roots, was found to be active against both yeast and filamentous fungi. Glabridin also showed resistance modifying activity against drug resistant mutants of Candida albicans at a minimum inhibitory conce... |
|
|
The inhibitory effect and the molecular mechanism of glabridin on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells.
Int. J. Mol. Med. 29(2) , 169-77, (2012) Osteoblastic bone formation and osteoclastic bone resorption are in balance to maintain a constant, homeostatically controlled amount of bone. Excessive bone resorption by osteoclasts is involved in the pathogenesis of bone-related disorders. In the present s... |
|
|
Glabridin protects osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells against antimycin A induced cytotoxicity.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 193(1) , 71-8, (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction, particularly respiratory chain disruption, is often responsible for aging-related bone diseases. In this study, the protective effects of glabridin, an isoflavan isolated from licorice root, against pharmacological inhibition of the... |
|
|
Glabridin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of a microglial cell line, BV-2, by blocking NF-kappaB and AP-1.
Phytother Res. 24 Suppl 1 , S29-34, (2010) Glabridin, a flavonoid present in licorice root, is known to have antiinflammatory and cardiovascular protective activities. The present study reports an inhibitory effect of glabridin on microglial activation. Glabridin dose-dependently attenuated lipopolysa... |
|
|
The flavonoid glabridin attenuates 2-deoxy-D-ribose-induced oxidative damage and cellular dysfunction in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells.
Int. J. Mol. Med. 31(1) , 243-51, (2013) Reducing sugar 2-deoxy-D-ribose (dRib) produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) through autoxidation and protein glycosylation and causes dysfunction of osteoblasts. In the present study, glabridin, a natural flavonoid, was investigated to determine whether it ... |