1,3-dichloropropene
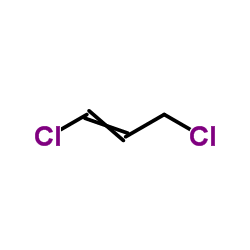
1,3-dichloropropene structure
|
Common Name | 1,3-dichloropropene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 542-75-6 | Molecular Weight | 110.970 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 108.4±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H4Cl2 | Melting Point | -60 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 27.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |




GHS02, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Halogenated derivatives QSAR model using spectral moments to predict haloacetic acids (HAA) mutagenicity.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 5720-32, (2008) The risk of the presence of haloacetic acids in drinking water as chlorination by-products and the shortage of experimental mutagenicity data for most of them requires a research work. This paper describes a QSAR model to predict direct mutagenicity for these... |
|
|
Laboratory assessment of emission reduction strategies for the agricultural fumigants 1,3-dichloropropene and chloropicrin.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(13) , 5073-8, (2009) With the increased use of the agricultural fumigants 1,3-dichloropropene (1,3-D) and chloropicrin (CP), it is important that strategies to reduce emissions of these fumigant from soil to the air are assessed to protect air quality. Using an established soil c... |
|
|
Mitigating 1,3-dichloropropene, chloropicrin, and methyl iodide emissions from fumigated soil with reactive film.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(11) , 6143-9, (2012) Implicated as a stratospheric ozone-depleting compound, methyl bromide (MeBr) is being phased out despite being considered to be the most effective soil fumigant. Its alternatives, i.e., 1,3-dichloropropene (1,3-D, which includes cis and trans isomers), chlor... |
|
|
Managing root-knot nematodes and weeds with 1,3-dichloropropene as an alternative to methyl bromide in cucumber crops in China.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(6) , 2362-7, (2011) 1,3-dichloropropene (1,3-D) was evaluated as a potential alternative for the widely used soil fumigant methyl bromide (MeBr) in cucumber (Cucumis sativus Linn.) crops in China. Six treatments were replicated five times in a randomized complete block design: f... |
|
|
Subsurface drip application of alternative fumigants to methyl bromide for controlling nematodes in replanted grapevines.
Pest Manag. Sci. 68(5) , 773-80, (2012) Many California grape growers use preplant fumigation to ensure uniform and healthy grapevine establishment in replant situations. A field study was conducted to evaluate the performance of subsurface drip-applied chemical alternatives to methyl bromide on pl... |
|
|
Evaluation of the combination of 1,3-dichloropropene and dazomet as an efficient alternative to methyl bromide for cucumber production in China.
Pest Manag. Sci. 68(4) , 602-9, (2012) The combination of 1,3-dichloropropene (1,3-D) and dazomet (DZ) offers a potential alternative to methyl bromide (MB) for soil disinfection. MB is scheduled to be withdrawn from routine use by 2015 in developing countries. Combination treatments of 1,3-D + DZ... |
|
|
Quantification of the effects of various soil fumigation treatments on nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in laboratory incubation and field studies.
Chemosphere 90(3) , 1210-5, (2013) Better quantification of nitrogen mineralization and nitrification after fumigation would indicate if any adjustment is needed in fertilizer application. The effects of chloropicrin (Pic), 1,3-dichloropropene (1,3-D), dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) and metham sodi... |
|
|
Spot fumigation: fumigant gas dispersion and emission characteristics.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(15) , 5783-9, (2009) Reducing emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from fumigant pesticides is mandatory in California, especially in "nonattainment areas" like the San Joaquin Valley that do not meet federal air quality standards. A two-year field study was conducted t... |
|
|
Field evaluation of a new plastic film (vapor safe) to reduce fumigant emissions and improve distribution in soil.
J. Environ. Qual. 40(4) , 1195-203, (2011) Preplant soil fumigation is an important pest management practice in coastal California strawberry production regions. Potential atmospheric emissions of fumigants from field treatment, however, have drawn intensive environmental and human health concerns; in... |
|
|
Interactive effect of organic amendment and environmental factors on degradation of 1,3-dichloropropene and chloropicrin in soil.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(19) , 9063-70, (2009) Soil organic matter is an important factor affecting the fate of soil fumigants; therefore, the addition of organic amendments to surface soils could reduce fumigant emissions by accelerating fumigant degradation. Experiments were conducted to determine the d... |