Phenacetin
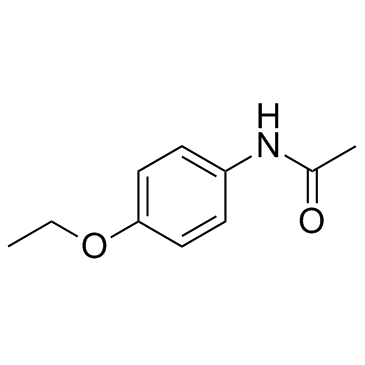
Phenacetin structure
|
Common Name | Phenacetin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 62-44-2 | Molecular Weight | 179.216 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 323.6±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13NO2 | Melting Point | 133-136 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 149.5±28.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
The Japanese toxicogenomics project: application of toxicogenomics.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 54 , 218-27, (2010) Biotechnology advances have provided novel methods for the risk assessment of chemicals. The application of microarray technologies to toxicology, known as toxicogenomics, is becoming an accepted approach for identifying chemicals with potential safety proble... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Effect of commercially available green and black tea beverages on drug-metabolizing enzymes and oxidative stress in Wistar rats.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 70 , 120-7, (2014) The effect of commercially available green tea (GT) and black tea (BT) drinks on drug metabolizing enzymes (DME) and oxidative stress in rats was investigated. Male Wistar rats were fed a laboratory chow diet and GT or BT drink for 5 weeks. Control rats recei... |
|
|
HepG2 cells as an in vitro model for evaluation of cytochrome P450 induction by xenobiotics.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 38 , 691-704, (2015) Although various in vitro assays have been developed to evaluate the cytochrome P450 (CYP)-inducing potential of drug candidates, there is a continuing need for the development of a reliable model in drug discovery. The objective of the present study was to c... |
|
|
Morphological behaviour and metabolic capacity of cryopreserved human primary hepatocytes cultivated in a perfused multiwell device.
Xenobiotica 45(1) , 29-44, (2014) 1. The quantitative prediction of the pharmacokinetic parameters of a drug from data obtained using human in vitro systems remains a significant challenge i.e. prediction of metabolic clearance in humans and estimation of the relative contribution of enzymes ... |
|
|
Schisandrol B protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibition of CYP-mediated bioactivation and regulation of liver regeneration.
Toxicol. Sci. 143(1) , 107-15, (2014) Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is the most frequent cause of drug-induced acute liver failure. Schisandra sphenanthera is a traditional hepato-protective Chinese medicine and Schisandrol B (SolB) is one of its major active constituents. In this study, the prot... |
|
|
Development of qualitative and quantitative analysis methods in pharmaceutical application with new selective signal excitation methods for 13 C solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance using 1 H T1rho relaxation time.
J. Pharm. Sci. 102(1) , 154-61, (2013) Most pharmaceutical drug substances and excipients in formulations exist in a crystalline or amorphous form, and an understanding of their state during manufacture and storage is critically important, particularly in formulated products. Carbon 13 solid-state... |