EDTA ferric sodium salt
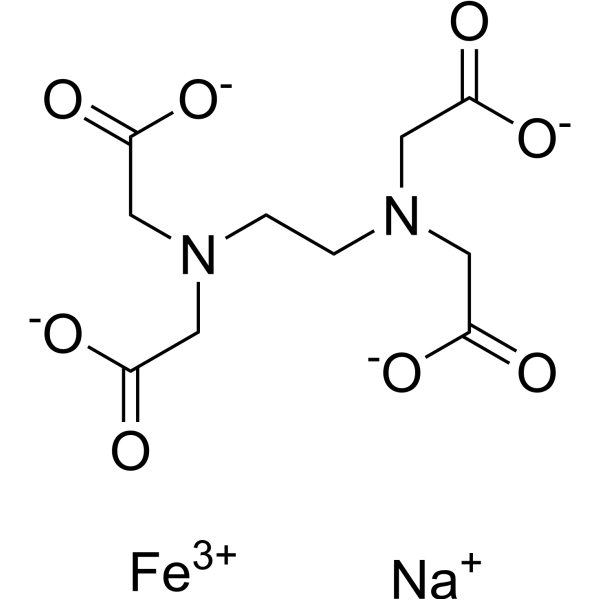
EDTA ferric sodium salt structure
|
Common Name | EDTA ferric sodium salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 15708-41-5 | Molecular Weight | 367.05 | |
| Density | 1.78 g/cm3 at 20 °C | Boiling Point | 614.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12FeN2NaO8 | Melting Point | 80 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 325.2ºC | |
|
Iron bioavailability from a lipid-based complementary food fortificant mixed with millet porridge can be optimized by adding phytase and ascorbic acid but not by using a mixture of ferrous sulfate and sodium iron EDTA.
J. Nutr. 143(8) , 1233-9, (2013) Home fortification with lipid-based nutrient supplements (LNSs) is a promising approach to improve bioavailable iron and energy intake of young children in developing countries. To optimize iron bioavailability from an LNS named complementary food fortificant... |
|
|
Sulfate removal by Desulfovibrio sp. CMX in chelate scrubbing solutions for NO removal.
Bioresour. Technol. 143 , 455-60, (2013) To study the effects of Fe chelate solution and nitrosyl-complex (Fe(II)EDTA-NO), which might be introduced in the simultaneous biodesulfurization and denitrification process, on the sulfate removal process, a sulfate reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio sp. CMX w... |
|
|
Simulation of the effect of maize porridge fortified with grain amaranth or micronutrient powder containing NaFeEDTA on iron intake and status in Kenyan children.
Publ. Health Nutr. 16(9) , 1605-13, (2013) Simulating the probable impact of grain amaranth and highly absorbable, low-Fe micronutrient powder (MNP) on Fe status in a potential target population is an essential step in choosing and developing an appropriate actual intervention.We simulated the potenti... |
|
|
Reduction of NOx in Fe-EDTA and Fe-NTA solutions by an enriched bacterial population.
Bioresour. Technol. 130 , 644-51, (2013) An enriched biomass was developed from municipal sewage sludge consisting of three dominant bacteria, representing the genera of Enterobacter, Citrobacter and Streptomyces. The biomass was used in a series of batch experiments in order to determine kinetic co... |
|
|
Fortification of wheat flour and maize meal with different iron compounds: results of a series of baking trials.
Food Nutr. Bull. 33(4 Suppl) , S344-59, (2012) Wheat and maize flour fortification is a preventive food-based approach to improve the micronutrient status of populations. In 2009, the World Health Organization (WHO) released recommendations for such fortification, with guidelines on the addition levels fo... |
|
|
Synthesis of Fe3O4 poly(styrene-glycidyl methacrylate) magnetic porous microspheres and application in the immobilization of Klebsiella sp. FD-3 to reduce Fe(III)EDTA in a NO(x) scrubbing solution.
Bioresour. Technol. 130 , 750-6, (2013) Magnetic poly(styrene-glycidyl methacrylate) porous microspheres (MPPM) with high magnetic contents were prepared by surfactant reverse micelles and emulsion polymerization of monomers, in which the well-dispersed Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticles were modified by poly... |
|
|
Accumulation and distribution of iron, cadmium, lead and nickel in cucumber plants grown in hydroponics containing two different chelated iron supplies.
J. Plant Physiol. 168(10) , 1038-44, (2011) Cucumber plants grown in hydroponics containing 10 μM Cd(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II), and iron supplied as Fe(III) EDTA or Fe(III) citrate in identical concentrations, were investigated by total-reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with special emphasis on t... |
|
|
Fortification of staple cereal flours with iron and other micronutrients: cost implications of following World Health Organization-endorsed recommendations.
Food Nutr. Bull. 33(4 Suppl) , S336-43, (2012) Wheat and maize flours are widely used delivery vehicles for mass fortification. In lower-income countries, most, if not all, national-level cereal flour fortification programs routinely fortify with iron; however, cofortification with other micronutrients is... |
|
|
Enhanced reduction of Fe(II)EDTA-NO/Fe(III)EDTA in NO(x) scrubber solution using a three-dimensional biofilm-electrode reactor.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(22) , 12640-7, (2012) A promising technique called chemical absorption-biological reduction (CABR) integrated approach has been developed recently for the nitrogen oxides (NO(x)) removal from flue gases. The major challenge for this approach is how to enhance the rate of the biolo... |
|
|
Reduction of Fe(III)EDTA(-) in a NO(x) scrubbing solution by magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan microspheres immobilized mixed culture of iron-reducing bacteria.
Bioresour. Technol. 108 , 169-75, (2012) Magnetic Fe(3)O(4)-chitosan microspheres were prepared by co-precipitating of Fe(2+) and Fe(3+) ions with NaOH in the presence of chitosan. The saturated magnetization of the resulting material was 20.0 emu/g. Then these magnetic microspheres were employed to... |