Reduction of Fe(III)EDTA(-) in a NO(x) scrubbing solution by magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan microspheres immobilized mixed culture of iron-reducing bacteria.
Guohua Jing, Jin Zhou, Zuoming Zhou, Tianming Lin
Index: Bioresour. Technol. 108 , 169-75, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Magnetic Fe(3)O(4)-chitosan microspheres were prepared by co-precipitating of Fe(2+) and Fe(3+) ions with NaOH in the presence of chitosan. The saturated magnetization of the resulting material was 20.0 emu/g. Then these magnetic microspheres were employed to immobilize iron-reducing bacteria to improve the biological reduction of Fe(III)EDTA(-), which was one of the key steps in nitrogen oxides (NO(x)) removal by the integrated chemical absorption-biological reduction process. The immobilized bacteria performed well on Fe(III)EDTA(-) reduction than free bacteria, even under unfavorable pH and temperatures. Furthermore, the effects of NO(2)(-), NO(3)(-), SO(3)(-), and S(2-), the potential inhibition compounds in the scrubber solution, on the reduction of Fe(III)EDTA(-) by the immobilized and free bacteria were also studied.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
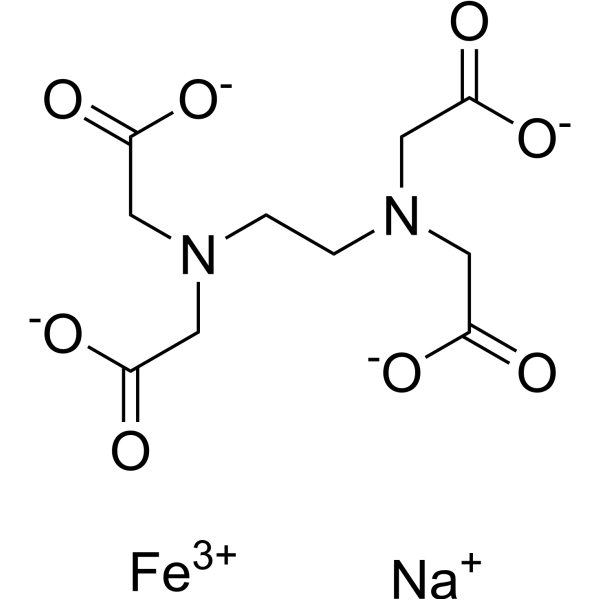 |
EDTA ferric sodium salt
CAS:15708-41-5 |
C10H12FeN2NaO8 |
|
Iron bioavailability from a lipid-based complementary food f...
2013-08-01 [J. Nutr. 143(8) , 1233-9, (2013)] |
|
Sulfate removal by Desulfovibrio sp. CMX in chelate scrubbin...
2013-09-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 143 , 455-60, (2013)] |
|
Simulation of the effect of maize porridge fortified with gr...
2013-09-01 [Publ. Health Nutr. 16(9) , 1605-13, (2013)] |
|
Reduction of NOx in Fe-EDTA and Fe-NTA solutions by an enric...
2013-02-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 130 , 644-51, (2013)] |
|
Fortification of wheat flour and maize meal with different i...
2012-12-01 [Food Nutr. Bull. 33(4 Suppl) , S344-59, (2012)] |