Xanthotoxin
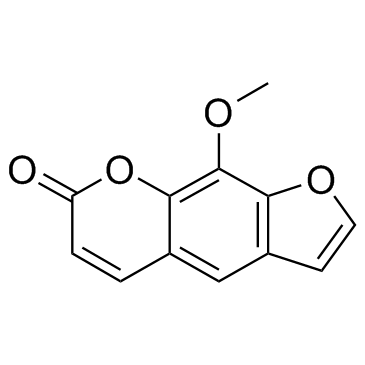
Xanthotoxin structure
|
Common Name | Xanthotoxin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 298-81-7 | Molecular Weight | 216.189 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 414.8±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H8O4 | Melting Point | 143-148 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 204.7±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Interspecies comparison of hepatic metabolism of six newly synthesized retinoid X receptor agonistic compounds possessing a 6-[N-ethyl-N-(alkoxyisopropylphenyl)amino]nicotinic acid skeleton in rat and human liver microsomes.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 40(8) , 1065-71, (2014) The hepatic metabolism of six compounds newly synthesized as retinoid X receptor agonists was characterized in rat and human liver microsomes to examine the relationship between their hepatic metabolism profiles and side chain structures, considering the inte... |
|
|
Chemical inhibitors of CYP450 enzymes in liver microsomes: combining selectivity and unbound fractions to guide selection of appropriate concentration in phenotyping assays.
Xenobiotica 45(2) , 95-106, (2014) 1. Chemical inhibition is the widely used method in reaction phenotyping assays for estimation of specific enzyme contribution to a given metabolic pathway. The results from phenotyping assays depend on the selectivity of chemical inhibitor and the concentrat... |
|
|
Cytochrome p450-mediated metabolic activation of diosbulbin B.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(10) , 1727-36, (2014) Diosbulbin B (DIOB), a furan-containing diterpenoid lactone, is the most abundant component of Dioscorea bulbifera L. (DB), a traditional Chinese medicine herb. Administration of purified DIOB or DB extracts has been reported to cause liver injury in animals.... |
|
|
Temporal endogenous gene expression profiles in response to lipid-mediated transfection.
J. Gene Med. 17(1-2) , 14-32, (2015) Design of efficient nonviral gene delivery systems is limited as a result of the rudimentary understanding of the specific molecules and processes that facilitate DNA transfer.Lipoplexes formed with Lipofectamine 2000 (LF2000) and plasmid-encoding green fluor... |
|
|
Extracorporeal photopheresis promotes IL-1β production.
J. Immunol. 194(6) , 2569-77, (2015) Extracorporeal photopheresis (ECP) is a widely used clinical cell-based therapy exhibiting efficacy in heterogenous immune-mediated diseases such as cutaneous T cell lymphoma, graft-versus-host disease, and organ allograft rejection. Despite its documented ef... |
|
|
[Chemical constituents contained in seeds of Notopterygium franchetii].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 37(7) , 941-5, (2012) To study the chemical constituents from the seeds of Notopterygium franchetii.Ethanol extracts of seeds N. franchetii were separated and purified by such methods as normal and reversed phase column chromatographies and thin-layer chromatography and structural... |
|
|
Characterization of phase I metabolism of resibufogenin and evaluation of the metabolic effects on its antitumor activity and toxicity.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43(3) , 299-308, (2015) Resibufogenin (RB), one of the major active compounds of the traditional Chinese medicine Chansu, has displayed great potential as a chemotherapeutic agent in oncology. However, it is a digoxin-like compound that also exhibits extremely cardiotoxic effects. T... |
|
|
Cytochrome p450 enzymes mechanism based inhibitors: common sub-structures and reactivity.
Curr. Drug Metab. 6 , 413-54, (2005) The inhibition of human cytochrome P450s (CYPs) is one of the most common mechanisms which can lead to drug-drug interactions. The inhibition of CYPs can be reversible (competitive or non-competitive) or irreversible. Irreversible inhibition usually derives f... |