Ethyl Mesilate
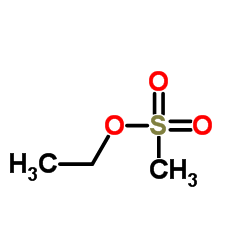
Ethyl Mesilate structure
|
Common Name | Ethyl Mesilate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 62-50-0 | Molecular Weight | 124.15 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 214.4±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H8O3S | Melting Point | < 25ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100.0±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Matrix precipitation: a general strategy to eliminate matrix interference for pharmaceutical toxic impurities analysis.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1379 , 16-23, (2015) Matrix interference, which can lead to false positive/negative results, contamination of injector or separation column, incompatibility between sample solution and the selected analytical instrument, and response inhibition or even quenching, is commonly suff... |
|
|
Safety assessment of dietary bamboo charcoal powder: a 90-day subchronic oral toxicity and mutagenicity studies.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 75 , 50-7, (2015) Vegetable carbon has been used as food additive in EU (E153) and China for many years; however, no experimental data have been available on its dietary safety. This study was designed to evaluate the subchronic toxicity and genotoxicity of bamboo charcoal pow... |
|
|
Radiation and chemical mutagen induced somaclonal variations through in vitro organogenesis of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).
Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 90(12) , 1229-39, (2014) The purpose of the investigation was to induce somaclonal variations by gamma rays (GR), ethylmethane sulphonate (EMS) and sodium azide (SA) during in vitro organogenesis of cotton.The shoot tip explants were irradiated with 5-50 Gray (Gy) GR (Cobalt 60), 0.5... |
|
|
Potent neutralization of vaccinia virus by divergent murine antibodies targeting a common site of vulnerability in L1 protein.
J. Virol. 88(19) , 11339-55, (2014) Vaccinia virus (VACV) L1 is an important target for viral neutralization and has been included in multicomponent DNA or protein vaccines against orthopoxviruses. To further understand the protective mechanism of the anti-L1 antibodies, we generated five murin... |
|
|
Mutagenic potential of the isoflavone irilone in cultured V79 cells.
Toxicol. Lett. 234(2) , 81-91, (2015) After consumption of red clover-based dietary supplements, plasma concentrations of the isoflavone irilone (IRI) equal that of the well-investigated daidzein. Since some isoflavones are genotoxic, the potential of IRI to induce mutations was investigated. Gen... |
|
|
Construction of a supF-based system for detection of mutations in the chromosomal DNA of Arabidopsis.
Mol. Genet. Genomics 288(12) , 707-15, (2013) The factors maintaining genomic integrity, which have been studied in detail in other species, have yet to be investigated in plants. Recent progress in gene-silencing technology has made it possible to produce transgenic plants with loss-of-function phenotyp... |
|
|
In vivo genotoxicity of Ginkgo biloba extract in gpt delta mice and constitutive androstane receptor knockout mice.
Toxicol. Sci. 140(2) , 298-306, (2014) The National Toxicology Program study of Ginkgo biloba extract (GBE), a herbal supplement, reported concerns regarding genotoxicity and clear evidence of hepatocarcinogenicity and liver hypertrophy in mice. To clarify the genotoxicity of GBE in vivo, we perfo... |
|
|
Quantitative assessment of the dose-response of alkylating agents in DNA repair proficient and deficient ames tester strains.
Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 55(1) , 15-23, (2014) Mutagenic and clastogenic effects of some DNA damaging agents such as methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) and ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) have been demonstrated to exhibit a nonlinear or even "thresholded" dose-response in vitro and in vivo. DNA repair seems to be... |
|
|
Cytoplasmic and nuclear toxicity of 3,5-dimethylaminophenol and potential protection by selenocompounds.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 72 , 98-110, (2014) Most common alkylanilines in the environment are 2,6-dimethylaniline (2,6-DMA), 3,5-dimethylaniline (3,5-DMA), and 3-ethylaniline (3-EA). 3,5-Dimethylaminophenol (3,5-DMAP), a metabolite of 3,5-DMA, is of particular interest, as it is potentially genotoxic. S... |
|
|
Combining molecular docking and 3-D pharmacophore generation to enclose the in vivo antigenotoxic activity of naturally occurring aromatic compounds: myricetin, quercetin, rutin, and rosmarinic acid.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 86(9) , 1376-96, (2013) Considering the controversial results concerning the antimutagenicity of some phenolic compounds recorded in the literature, the antigenotoxic effects of four selected phenolic compounds, myricetin, quercetin, rutin, and rosmarinic acid, against DNA damage in... |