N-(2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl)-D-cysteine
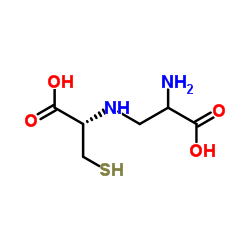
N-(2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl)-D-cysteine structure
|
Common Name | N-(2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl)-D-cysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3183-08-2 | Molecular Weight | 208.236 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 462.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12N2O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 233.5±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Nine post-translational modifications during the biosynthesis of cinnamycin.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 , 13753-13760, (2011) Lantibiotics are ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified antimicrobial peptides that are characterized by the thioether cross-linked amino acids lanthionine (Lan) and methyllanthionine (MeLan). Cinnamycin is a 19 amino acid lantibiotic that ... |
|
|
Substrate recognition and specificity of the NisB protein, the lantibiotic dehydratase involved in nisin biosynthesis.
J. Biol. Chem. 286 , 30552-30560, (2011) Nisin is a posttranslationally modified antimicrobial peptide containing the cyclic thioether amino acids lanthionine and methyllanthionine. Although much is known about its antimicrobial activity and mode of action, knowledge about the nisin modification pro... |
|
|
Leader peptide-directed processing of labyrinthopeptin A2 precursor peptide by the modifying enzyme LabKC.
Biochemistry 50 , 8362-8373, (2011) Lantibiotics are peptide antibiotics, realizing their unique secondary structure by posttranslational modifications, the most important one being the formation of the characteristic amino acid lanthionine. Like other ribosomal peptide antibiotics, they are sy... |
|
|
Methodologies and strategies for the bioengineering of lantibiotics.
Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 12 , 1221-1230, (2011) Lantibiotics are ribosomally synthesized, post-translationally modified, peptide antibiotics containing unusual amino acids such as dehydrated amino acids and lanthionine. These unusual amino acids impose conformational constraints on the peptide and contribu... |
|
|
Autocrine abscisic acid mediates the UV-B-induced inflammatory response in human granulocytes and keratinocytes. Bruzzone S, Basile G, Mannino E, et al.
J. Cell Physiol. 227(6) , 2502-10, (2011)
|