5-Fluoroindole-2-carboxylic acid
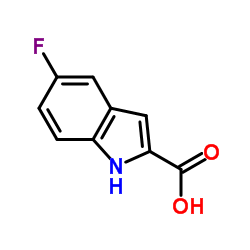
5-Fluoroindole-2-carboxylic acid structure
|
Common Name | 5-Fluoroindole-2-carboxylic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 399-76-8 | Molecular Weight | 179.148 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 422.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6FNO2 | Melting Point | 259 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 209.1±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of novel and diverse cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors as anti-inflammatory drugs.
J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 29(6) , 846-67, (2014) Because of the pivotal role of cyclooxygenase (COX) in the inflammatory processes, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that suppress COX activities have been used clinically for the treatment of inflammatory diseases/syndromes; however, traditional... |
|
|
Stable benzotriazole esters as mechanism-based inactivators of the severe acute respiratory syndrome 3CL protease.
Chem. Biol. 13(3) , 261-8, (2006) Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by a newly emerged coronavirus that infected more than 8000 individuals and resulted in more than 800 fatalities in 2003. Currently, there is no effective treatment for this epidemic. SARS-3CL(pro) has been s... |
|
|
Effect of 5-fluoroindole-2-carboxylic acid (an antagonist of the NMDA receptor-associated glycine site) on the anticonvulsive activity of conventional antiepileptic drugs.
J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 105(2-3) , 133-46, (1998) 5-Fluoroindole-2-carboxylic acid, an antagonist of the glycine site within the NMDA receptor complex, administered intraperitoneally in doses of 150 and 200 mg/kg, 120 min before electroconvulsions, significantly raised the convulsive threshold from 6.8 to 7.... |
|
|
Quisqualate activates N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in hippocampal neurons maintained in culture.
Mol. Pharmacol. 37(4) , 477-81, (1990) Whole-cell and single-channel patch-clamp recordings from hippocampal neurons in culture have been used to study the receptor channel selectivity of the glutamate analog quisqualate. The dose-response relationship of quisqualate acting at the N-methyl-D-aspar... |
|
|
Enhanced sensitivity of medullary depressor neurons to N-methyl-D-aspartate-glycine site antagonists in the spontaneously hypertensive rat.
Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 25(3-4) , 216-9, (1998) 1. The effects of the specific N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-glycine site antagonist 5-fluoro indole-2-carboxylic acid (FICA) and NMDA, microinjected into the vasodepressor caudal ventrolateral medulla, were compared in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and... |
|
|
Blockade of the glycine modulatory site of NMDA receptors modifies dynorphin-induced behavioral effects.
Neurosci. Lett. 110(1-2) , 113-7, (1990) Intrathecal (i.t.) administration of the opioid dynorphin causes neurological dysfunction and tissue damage. It has been suggested that these effects of dynorphin may be mediated, in part, by N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. In the present studies, rece... |