Isopropyl palmitate
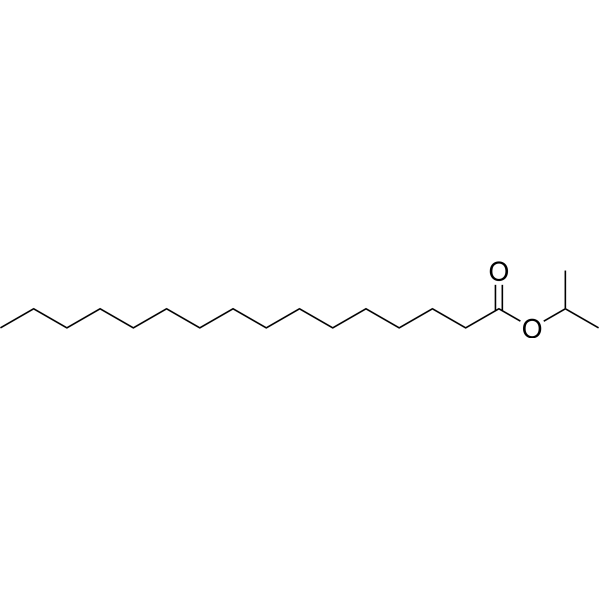
Isopropyl palmitate structure
|
Common Name | Isopropyl palmitate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 142-91-6 | Molecular Weight | 298.51 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 340.7±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H38O2 | Melting Point | 11-13 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 162.2±8.8 °C | |
|
Transdermal delivery of curcumin via microemulsion.
Int. J. Pharm. 481(1-2) , 97-103, (2015) The objective of this study was to evaluate the transdermal delivery potential of a new curcumin-containing microemulsion system. Three series of experiments were carried out to comprehend the system characteristics: (a) examining the influence of water conte... |
|
|
Comparative percutaneous permeation study using caffeine-loaded microemulsion showing low reliability of the frozen/thawed skin models.
Int. J. Pharm. 471(1-2) , 516-24, (2014) The aim of this study was to explore the transdermal delivery potential of a new caffeine-containing microemulsion system. The skin permeability of caffeine (CAF) was measured in vitro using skin excised from three different animal species: rat, rabbit and pi... |
|
|
Transcutaneous delivery of leflunomide nanoemulgel: Mechanistic investigation into physicomechanical characteristics, in vitro anti-psoriatic and anti-melanoma activity.
Int. J. Pharm. 487 , 148-56, (2015) The present study is a mechanistic validation of 'proof of concept' of effective topical delivery of leflunomide (LFD) nanoemulgel for localized efficient treatment of psoriatic lesions as well as melanoma affected skin regions. Hyperproliferation of keratino... |
|
|
Kinetically stable propofol emulsions with reduced free drug concentration for intravenous delivery.
Int. J. Pharm. 486 , 232-41, (2015) Intravenous injections of propofol emulsions are accompanied by pain likely due to the interaction of the dissolved drug with endothelial cells of the vasculature. It is commonly hypothesized that reducing the aqueous phase concentration of propofol could red... |
|
|
Effects of isopropyl palmitate on the skin permeation of drugs.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(11) , 2324-6, (2006) The model penetrants oxaprozin, nimesulide, gliclazide, and ribavirin, because of their different lipophilicities, were selected to assess the enhancing activity of pre-treatment solutions consisting of isopropyl palmitate (IP) in ethanol (5%, 10%, 15%and 20%... |
|
|
Skin penetration and photoprotection of topical formulations containing benzophenone-3 solid lipid microparticles prepared by the solvent-free spray-congealing technique.
J. Microencapsul. 31(7) , 644-53, (2014) Solid-lipid microparticles loaded with high amounts of the sunscreen UV filter benzophenone-3 were prepared by spray congealing with the objective of decreasing its skin penetration and evaluate whether the sunscreen's photoprotection were impaired by the mic... |
|
|
Assessment of oil polarity: comparison of evaluation methods.
Int. J. Pharm. 348(1-2) , 89-94, (2008) In multiple emulsion systems, oily or aqueous transfers may occur between the dispersed droplets through the continuous phase. These transfers are controlled by both the surfactant system (micellar transport), and the partial solubility of one phase in anothe... |
|
|
Transdermal delivery of hydrophobic and hydrophilic local anesthetics from o/w and w/o Brij 97-based microemulsions.
J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 10(3) , 288-98, (2007) To characterize the physicochemical properties of drug-loaded oil-in-water (o/w) and water-in-oil (w/o) Brij 97-based microemulsions in comparison to their blank counterparts and to investigate the influence of microemulsion type on in vitro skin permeation o... |
|
|
Characterization of microemulsion structures in the pseudoternary phase diagram of isopropyl palmitate/water/Brij 97:1-butanol.
AAPS PharmSciTech 7(2) , E45, (2006) This research was aimed to characterize microemulsion systems of isopropyl palmitate (IPP), water, and 2:1 Brij 97 and 1-butanol by different experimental techniques. A pseudoternary phase diagram was constructed using water titration method. At 45% wt/wt sur... |
|
|
Preparation and evaluation of diltiazem hydrochloride diffusion-controlled transdermal delivery system.
AAPS PharmSciTech 9(2) , 464-70, (2008) The objective was to investigate the suitable polymeric films for the development of diltiazem hydrochloride (diltiazem HCl) transdermal drug delivery systems. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and ethylcellulose (EC) were used as hydrophilic and hydrophob... |