Methyl α-D-mannopyranoside
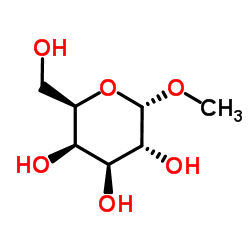
Methyl α-D-mannopyranoside structure
|
Common Name | Methyl α-D-mannopyranoside | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3396-99-4 | Molecular Weight | 194.182 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 389.1±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H14O6 | Melting Point | 116-117 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 189.1±27.9 °C | |
|
Metal-mediated allylation of enzymatically oxidized methyl α-d-galactopyranoside
Carbohydr. Res. 345 , 2610-5, (2010) The C-6 unit of methyl α-D-galactopyranoside was selectively modified by combining enzymatic oxidation with an indium-mediated allylation reaction. The Barbier-Grignard type reaction, where a carbonyl group reacts with an allyl halide, proceeds in aqueous sol... |
|
|
alpha-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of triterpenoids from Cichorium intybus.
J. Nat. Prod. 71 , 910-3, (2008) Two new triterpenoids, 18alpha,19beta-20(30)-taraxasten-3beta,21alpha-diol (cichoridiol) (1) and 17-epi-methyl-6-hydroxyangolensate (intybusoloid) (2), were obtained from the methanolic extract of seeds of Cichorium intybus along with 11 known compounds, lupe... |
|
|
1-O-Acetyl-beta-D-galactopyranose: a novel substrate for the transglycosylation reaction catalyzed by the beta-galactosidase from Penicillium sp.
Carbohydr. Res. 337(7) , 635-42, (2002) 1-O-Acetyl-beta-D-galactopyranose (AcGal), a new substrate for beta-galactosidase, was synthesized in a stereoselective manner by the trichloroacetimidate procedure. Kinetic parameters (K(M) and k(cat)) for the hydrolysis of 1-O-acetyl-beta-D-galactopyranose ... |
|
|
The interaction of elderberry (Sambucus sieboldiana) bark lectin and sialyloligosaccharides as detected by 1H-NMR.
J. Biochem. 112(1) , 143-6, (1992) The interaction of Japanese elderberry bark lectin (Sambucus sieboldiana agglutinin, SSA) with carbohydrate was investigated by 1H-NMR. When a low affinity ligand, methyl beta-D-galactoside (beta MeGal), was mixed with SSA, each proton signal of beta MeGal wa... |
|
|
Molecular analysis and anticonvulsant therapy in two patients with glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome: a successful use of zonisamide for controlling the seizures.
Epilepsy Res. 80(1) , 18-22, (2008) Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) deficiency syndrome is caused by a deficit in glucose transport to the brain during the pre- and postnatal periods. Here, we report two cases of GLUT1 deficiency syndrome diagnosed on the basis of clinical features, reduced GLUT1... |
|
|
DNA polymerase-associated lectin (DPAL) and its binding to the galactose-containing glycoconjugate of the replication complex.
Biosci. Rep. 19(5) , 433-47, (1999) The highly purified DNA Pol-alpha from rat prostate tumor (PA-3) and human neuroblastoma (IMR-32) cells appeared to be inhibited by Ricin (RCA-II), and Con-A. Loss of activity (40 to 60%) of a specific form of DNA polymerase from IMR-32 was observed when the ... |
|
|
A 45-kDa midgut glycoprotein from Anopheles albimanus mosquito mediates the killing of trypanosomes.
Cell Biochem. Funct. 20(3) , 257-62, (2002) Trypanosomes do not inhabit or grow in anopheles mosquitoes, the vector for the transmission of Plasmodium parasites the causative agent for malaria. The possession of lytic factors by the anopheline mosquito was thus considered. Head and midgut sections prep... |
|
|
NMR spectroscopy of hydroxyl protons in supercooled carbohydrates.
Nat. Struct. Biol. 1(4) , 215-6, (1994)
|
|
|
Primary structure determination of seven novel N-linked carbohydrate chains derived from hemocyanin of Lymnaea stagnalis. 3-O-methyl-D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine as constituents of xylose-containing N-linked oligosaccharides in an animal glycoprotein.
Eur. J. Biochem. 169(2) , 399-411, (1987) Hemocyanin from the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis is a high-molecular-mass copper-containing glyco-protein which functions as oxygen carrier in the hemolymph. To release the carbohydrate chains, the protein was digested by pronase followed by hydrazinoly... |
|
|
Glycolipids as receptors for Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin.
Science 307(5711) , 922-5, (2005) The development of pest resistance threatens the effectiveness of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxins used in transgenic and organic farming. Here, we demonstrate that (i) the major mechanism for Bt toxin resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans entails a loss of ... |