| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Methyl β-D-galactopyranoside
CAS:1824-94-8 |
|
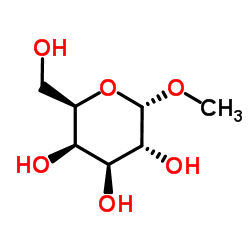 |
Methyl α-D-mannopyranoside
CAS:3396-99-4 |