Calcium gluconate
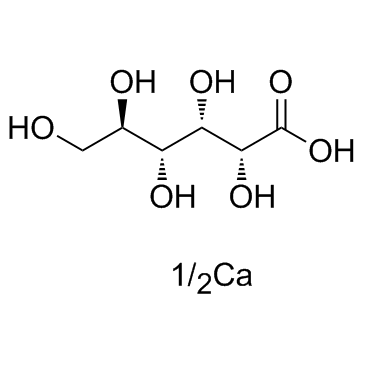
Calcium gluconate structure
|
Common Name | Calcium gluconate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 299-28-5 | Molecular Weight | 216.20 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 673.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O7.1/2Ca | Melting Point | 195°C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 375.2ºC | |
|
Calcium Chloride in Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Solutions with and without Added Cysteine: Compatibility Studies Using Laser and Micro-Flow Imaging Methodology.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0136894, (2015) Previous studies of compatibility of calcium chloride (CaCl2) and phosphates have not included particle counts in the range specified by the United States Pharmacopeia. Micro-flow imaging techniques have been shown to be comparable to light obscuration when d... |
|
|
Dietary calcium deficiency and excess both impact bone development and mesenchymal stem cell lineage priming in neonatal piglets.
J. Nutr. 144(12) , 1935-42, (2014) Optimizing calcium nutrition to maximize bone accretion during growth to prevent fragility fractures later in life has spurred greater interest in calcium nutrition in neonates.The aim of this study was to determine the effect of dietary calcium, from deficie... |
|
|
Goshajinkigan, a traditional Japanese medicine, prevents oxaliplatin-induced acute peripheral neuropathy by suppressing functional alteration of TRP channels in rat.
J. Pharmacol. Sci. 125(1) , 91-8, (2014) The acute peripheral neuropathy induced by oxaliplatin treatment occurs very frequently and is aggravated by exposure to cold. Goshajinkigan (GJG), a traditional Japanese (kampo) medicine, was recently shown to be effective against oxaliplatin-induced acute n... |
|
|
Gingival pain: an unusual side effect of ziprasidone.
BMJ Case Rep. 2013 , doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007577, (2013) The patient is a 52-year-old man with schizophrenia who developed severe, unremitting gingival pain after his ziprasidone dosage was increased from 80 to 120 mg. His physical examination and laboratory findings were unremarkable. He did not have any extra-pyr... |
|
|
Early life exposure to chronic intermittent hypoxia causes upper airway dilator muscle weakness, which persists into young adulthood.
Exp. Physiol. 100 , 947-66, (2015) What is the central question of this study? Chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) is a dominant feature of respiratory control disorders, which are common. We sought to examine the effects of exposure to CIH during neonatal development on respiratory muscle form... |
|
|
Stability of hydrophilic vitamins mixtures in the presence of electrolytes and trace elements for parenteral nutrition: a nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy investigation.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 107 , 7-10, (2015) In total parenteral nutrition (TPN), especially in the case of preterm infants, simultaneous administration of vitamins and trace elements is still a problematic issue: guidelines put in evidence the lack of specific documentation. In this work NMR spectrosco... |
|
|
Human organic anion transporter 2 is distinct from organic anion transporters 1 and 3 with respect to transport function.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 309 , F843-51, (2015) Phylogentically, organic anion transporter (OAT)1 and OAT3 are closely related, whereas OAT2 is more distant. Experiments with human embryonic kidney-293 cells stably transfected with human OAT1, OAT2, or OAT3 were performed to compare selected transport prop... |
|
|
Estimating the value of intravenous calcium and magnesium in ameliorating oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy.
J. Clin. Oncol. 32(29) , 3341, (2014)
|
|
|
Hydrofluoric acid exposure: a case report and review on the clinical presentation and management.
Dermatitis 23(5) , 231-6, (2012) Exposure to hydrofluoric acid can cause severe skin damage via both corrosive and chemical means. Dermatologists should be aware of the various clinical presentations and knowledgeable of how to manage such patients. A case of a man with exposure of the hands... |
|
|
Electrolyte imbalances and nephrocalcinosis in acute phosphate poisoning on chronic type 1 renal tubular acidosis due to Sjögren's syndrome.
J. Korean Med. Sci. 28(2) , 336-9, (2013) Although renal calcium crystal deposits (nephrocalcinosis) may occur in acute phosphate poisoning as well as type 1 renal tubular acidosis (RTA), hyperphosphatemic hypocalcemia is common in the former while normocalcemic hypokalemia is typical in the latter. ... |