| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
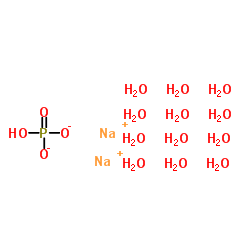 |
Disodium phosphate dodecahydrate
CAS:10039-32-4 |
|
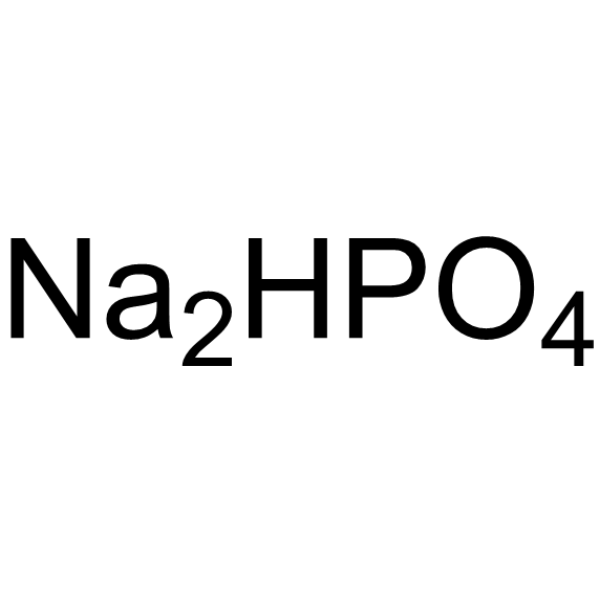 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
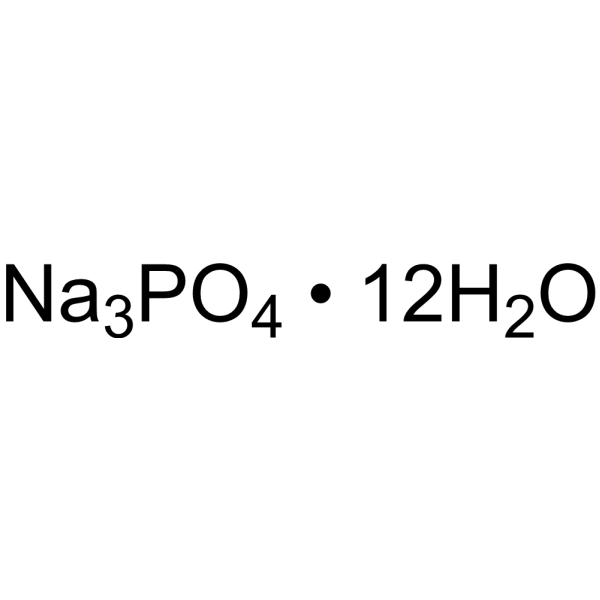 |
Trisodium phosphate dodecahydrate
CAS:10101-89-0 |
|
 |
sodium dihydrogenphosphate
CAS:7558-80-7 |
|
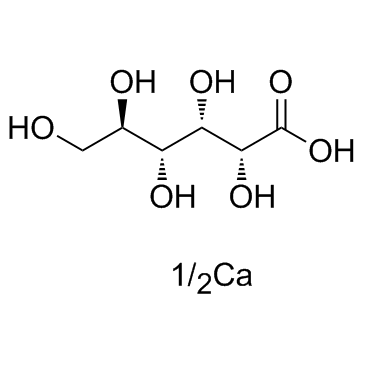 |
Calcium gluconate
CAS:299-28-5 |
|
 |
trisodium phosphate
CAS:7601-54-9 |
|
 |
Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate
CAS:7782-85-6 |