Linezolid
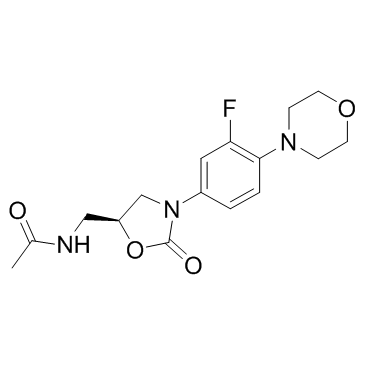
Linezolid structure
|
Common Name | Linezolid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 165800-03-3 | Molecular Weight | 337.346 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 585.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H20FN3O4 | Melting Point | 176-1780C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 307.9±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Complete genome sequencing and comparative analysis of the linezolid-resistant Enterococcus faecalis strain DENG1.
Arch. Microbiol. 196(7) , 513-6, (2014) Genome level analysis of bacterial strains provides information on genetic composition and resistance mechanisms to clinically relevant antibiotics. To date, whole genome characterization of linezolid-resistant Enterococcus faecalis isolated in the clinic is ... |
|
|
Gingival pain: an unusual side effect of ziprasidone.
BMJ Case Rep. 2013 , doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007577, (2013) The patient is a 52-year-old man with schizophrenia who developed severe, unremitting gingival pain after his ziprasidone dosage was increased from 80 to 120 mg. His physical examination and laboratory findings were unremarkable. He did not have any extra-pyr... |
|
|
Once-weekly dalbavancin versus daily conventional therapy for skin infection.
N. Engl. J. Med. 370(23) , 2169-79, (2014) Dalbavancin, a lipoglycopeptide antibiotic agent that is active against gram-positive pathogens, has a long plasma half-life, allowing for once-weekly dosing. DISCOVER 1 and DISCOVER 2 were identically designed noninferiority trials of dalbavancin for the tre... |
|
|
Evaluation of the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia.
Am. J. Med. Sci. 349(1) , 36-41, (2015) Bloodstream infections are a leading cause of death in the United States. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) encompasses >50% of all S aureus strains in infected hospitalized patients and increases mortality, length of stay and healthcare cost... |
|
|
Antimicrobial/anti-biofilm activity of expired blood platelets and their released products.
Postepy. Hig. Med. Dosw. 67 , 321-5, (2013) Although platelets are not part of the classical immune system, they have many features that indicate their role in the anti-infective host defense. They come into interactions with microorganisms, which results in co-aggregation and co-adhesion or destructio... |
|
|
Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus obtained from Southeast of Iran (Kerman).
APMIS 122(5) , 405-11, (2014) Staphylococcus aureus infections, particularly infections caused by methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains, are emerging as a major public health problem. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of MRSA, antibiotic resistance profile and... |
|
|
Clinical management of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a review.
JAMA 312(13) , 1330-41, (2014) Several management strategies may improve outcomes in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia.To review evidence of management strategies for S. aureus bacteremia to determine whether transesophageal echocardiography is necessary in all adult cases and... |
|
|
Novel drug combination for Mycobacterium abscessus disease therapy identified in a Drosophila infection model.
J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69(6) , 1599-607, (2014) Mycobacterium abscessus is known to be the most drug-resistant Mycobacterium and accounts for ∼80% of pulmonary infections caused by rapidly growing mycobacteria. This study reports a new Drosophila melanogaster-M. abscessus infection model that can be used a... |
|
|
A 12-year survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in Greece: ST80-IV epidemic?
Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 20(11) , O796-803, (2014) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an important cause of both healthcare-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA) and community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) infections. Severe MRSA infections have been associated with the virulence factor Panton-Valentine le... |
|
|
A practical guide to community-acquired MRSA.
J. Fam. Pract. 62(11) , 624-9, (2013) As the number of CA-MRSA skin and soft tissue infections continues to grow, it's important to know which patients are at greatest risk and which evidence-based treatment protocols to turn to when needed. |