Glyoxal
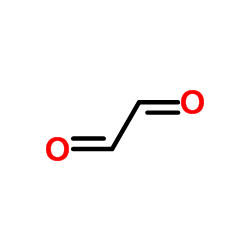
Glyoxal structure
|
Common Name | Glyoxal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 107-22-2 | Molecular Weight | 58.036 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 50.0±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H2O2 | Melting Point | -14 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | -4.3±4.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Yeast Coq9 controls deamination of coenzyme Q intermediates that derive from para-aminobenzoic acid.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1851 , 1227-39, (2015) Coq9 is a polypeptide subunit in a mitochondrial multi-subunit complex, termed the CoQ-synthome, required for biosynthesis of coenzyme Q (ubiquinone or Q). Deletion of COQ9 results in dissociation of the CoQ-synthome, but over-expression of Coq8 putative kina... |
|
|
Structural diversity of supercoiled DNA.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 8440, (2015) By regulating access to the genetic code, DNA supercoiling strongly affects DNA metabolism. Despite its importance, however, much about supercoiled DNA (positively supercoiled DNA, in particular) remains unknown. Here we use electron cryo-tomography together ... |
|
|
Novel HPLC--Fluorescence methodology for the determination of methylglyoxal and glyoxal. Application to the analysis of monovarietal wines "Ribera del Guadiana".
Food Chem. 187 , 159-65, (2015) The determination and quantification of α-dicarbonyl compounds, glyoxal and methylglyoxal, in "Ribera del Guadiana" monovarietal wines (Extremadura, Spain) without sample clean-up has been carried out by HPLC with spectrofluorimetric detection (307/371 nm). F... |
|
|
Anti-miRs competitively inhibit microRNAs in Argonaute complexes.
PLoS ONE 9(7) , e100951, (2014) MicroRNAs (miRNAs), small RNA molecules that post-transcriptionally regulate mRNA expression, are crucial in diverse developmental and physiological programs and their misregulation can lead to disease. Chemically modified oligonucleotides have been developed... |
|
|
GlxA is a new structural member of the radical copper oxidase family and is required for glycan deposition at hyphal tips and morphogenesis of Streptomyces lividans.
Biochem. J. 469 , 433-44, (2015) Streptomyces lividans displays a distinct dependence on copper to fully initiate morphological development. Evidence has accumulated to implicate the participation of an extracytoplasmic cuproenzyme in morphogenesis. In the present study, we show that GlxA fu... |
|
|
Dual mode signaling responses of a rhodamine based probe and its immobilization onto a silica gel surface for specific mercury ion detection.
Dalton Trans. 44 , 15304-15, (2015) A 3-aminomethyl-(2-amino-1-pyridyl) coupled amino-ethyl-rhodamine-B based probe (2) exhibited simultaneous chromogenic and fluorogenic dual mode signaling responses in the presence of Hg(II) ions only among all the metal ions investigated in an organic aqueou... |
|
|
Dual-phase osteogenic and vasculogenic engineered tissue for bone formation.
Tissue Eng. Part A 21(3-4) , 530-40, (2015) Minimally invasive, injectable bone tissue engineering therapies offer the potential to facilitate orthopedic repair procedures, including in indications where enhanced bone regeneration is needed for complete healing. In this study, we developed a dual-phase... |
|
|
Studies on the Formation of Maillard and Caramelization Products from Glucosamine Incubated at 37 °C.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 6249-61, (2015) This experiment compared the in vitro degradation of glucosamine (GlcN), N-acetylglucosamine, and glucose in the presence of NH3 incubated at 37 °C in phosphate buffer from 0.5 to 12 days. The reactions were monitored with UV-vis absorption and fluorescence e... |
|
|
Biologically active and thermally stable polymeric Schiff base and its metal polychelates: Their synthesis and spectral aspects.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 148 , 435-43, (2015) New metal polychelates of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) obtained by the interaction of metal acetates with polymeric Schiff base containing formaldehyde and piperazine, have been investigated. Structural and spectroscopic properties have been eval... |
|
|
Permeation of Hydrophilic Molecules across Glycated Skin Is Differentially Regulated by the Stratum Corneum and Epidermis-Dermis.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38 , 1383-8, (2015) The effects of glycation on skin permeation and accumulation of compounds were evaluated using an in vitro glycated skin model. Glycation of the skin of hairless mice was induced using vertical diffusion cells and incubation with phosphate-buffered saline con... |