Dichloroacetyl chloride
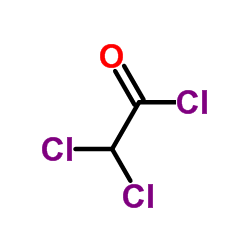
Dichloroacetyl chloride structure
|
Common Name | Dichloroacetyl chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79-36-7 | Molecular Weight | 147.388 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 107.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2HCl3O | Melting Point | < 25ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 31.8±22.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Halogenated derivatives QSAR model using spectral moments to predict haloacetic acids (HAA) mutagenicity.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 5720-32, (2008) The risk of the presence of haloacetic acids in drinking water as chlorination by-products and the shortage of experimental mutagenicity data for most of them requires a research work. This paper describes a QSAR model to predict direct mutagenicity for these... |
|
|
Autoimmune response in MRL+/+ mice following treatment with dichloroacetyl chloride or dichloroacetic anhydride.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 216(2) , 248-55, (2006) Dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) is formed from trichloroethene (TCE), which is implicated in inducing/accelerating autoimmune response. Due to its potent acylating activity, DCAC may convert proteins to neo-antigens and thus could induce autoimmune responses. ... |
|
|
Photocatalysis of gaseous trichloroethylene (TCE) over TiO2: the effect of oxygen and relative humidity on the generation of dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) and phosgene.
J. Hazard. Mater. 146(1-2) , 302-8, (2007) Batch photocatalytic degradation of 80+/-2.5 ppm V trichloroethylene (TCE) was conducted to investigate the effect of the oxygen and relative humidity (RH) on the formation of the dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) and phosgene. Based on the simultaneous ordinary... |
|
|
Anti-malondialdehyde antibodies in MRL+/+ mice treated with trichloroethene and dichloroacetyl chloride: possible role of lipid peroxidation in autoimmunity.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 170(2) , 88-92, (2001) Trichloroethene (TCE) and one of its metabolites dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) are known to induce/accelerate autoimmune (AI) response in MRL+/+ mice as evident from anti-nuclear, anti-ssDNA, anti-cardiolipin, and DCAC-specific antibodies in the serum (Khan ... |
|
|
Inhalation carcinogenesis of various alkylating agents.
J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 79(2) , 285-9, (1987) A series of earlier studies showed that inhalation exposures of rats to three water-reactive electrophilic compounds produced brisk yields of nasal cancer even when the animals were exposed for only 30 days (6 hr/day X 5 day/wk). In addition, carcinogenic pot... |
|
|
Transcriptomic analysis reveals early signs of liver toxicity in female MRL +/+ mice exposed to the acylating chemicals dichloroacetyl chloride and dichloroacetic anhydride.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 21(3) , 572-82, (2008) Dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) is a reactive metabolite of trichloroethene (TCE). TCE and its metabolites have been implicated in the induction of organ-specific and systemic autoimmunity, in the acceleration of autoimmune responses, and in the development of... |
|
|
Time-dependent autoimmune response of dichloroacetyl chloride in female MRL +/+ mice.
Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 19(2) , 265-77, (1997) Welders are exposed to dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) when trichloroethene (TCE) is used as a degreasing agent. Human exposure to TCE and tetrachloroethane can also lead to formation of DCAC in situ through metabolism. Due to its strong acylating property, it... |