Camostat Mesylate
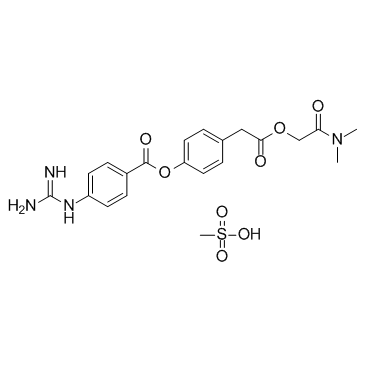
Camostat Mesylate structure
|
Common Name | Camostat Mesylate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59721-29-8 | Molecular Weight | 494.518 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 634.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H26N4O8S | Melting Point | 150-1550C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
ERK activation is required for CCK-mediated pancreatic adaptive growth in mice.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 307(7) , G700-10, (2014) High levels of cholecystokinin (CCK) can stimulate pancreatic adaptive growth in which mature acinar cells divide, leading to enhanced pancreatic mass with parallel increases in protein, DNA, RNA, and digestive enzyme content. Prolonged release of CCK can be ... |
|
|
Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry.
Antiviral Res. 116 , 76-84, (2015) In order to gain entry into cells, diverse viruses, including Ebola virus, SARS-coronavirus and the emerging MERS-coronavirus, depend on activation of their envelope glycoproteins by host cell proteases. The respective enzymes are thus excellent targets for a... |
|
|
Correction of defective CFTR/ENaC function and tightness of cystic fibrosis airway epithelium by amniotic mesenchymal stromal (stem) cells.
J. Cell. Mol. Med. 18(8) , 1631-43, (2014) Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, with most of the mortality given by the lung disease. Human amniotic mesenchymal stromal (stem) cells (hAMSCs) hold great promise for regenerative medicine ... |
|
|
Camostat mesilate attenuates pancreatic fibrosis via inhibition of monocytes and pancreatic stellate cells activity.
Lab. Invest. 85(1) , 75-89, (2005) Camostat mesilate (CM), an oral protease inhibitor, has been used clinically for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis in Japan. However, the mechanism by which it operates has not been fully understood. Our aim was to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of CM ... |