Difenacoum
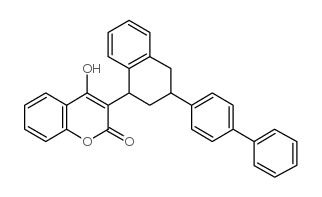
Difenacoum structure
|
Common Name | Difenacoum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56073-07-5 | Molecular Weight | 444.52000 | |
| Density | 1.272 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 612.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H24O3 | Melting Point | 96-98°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 204.3ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Fast targeted analysis of 132 acidic and neutral drugs and poisons in whole blood using LC-MS/MS.
Forensic Sci. Int. 243 , 35-43, (2014) The aim of this study was to develop an LC-MS/MS based screening technique that covers a broad range of acidic and neutral drugs and poisons by combining a small sample volume and efficient extraction technique with simple automated data processing. After pro... |
|
|
Use of two halogenated biphenyls as indicators of non-target exposure during rodenticide treatments.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 54(4) , 526-33, (1995)
|
|
|
Spatial and temporal analysis of second-generation anticoagulant rodenticide residues in polecats (Mustela putorius) from throughout their range in Britain, 1992-1999.
Environ. Pollut. 122(2) , 183-93, (2003) Polecats (Mustela putorius) in Britain are currently expanding their range eastwards from Wales to reoccupy central and eastern areas of England. Second-generation anticoagulant rodenticides (SGARs), to which polecats are exposed by eating contaminated prey, ... |
|
|
High exposure rates of anticoagulant rodenticides in predatory bird species in intensively managed landscapes in Denmark.
Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 63(3) , 437-44, (2012) The extensive use of anticoagulant rodenticides (ARs) for rodent control has led to widespread secondary exposure in nontarget predatory wildlife species. We investigated exposure rates and concentrations of five ARs in liver samples from five raptors and six... |
|
|
Concentrations of anticoagulant rodenticides in stoats Mustela erminea and weasels Mustela nivalis from Denmark.
Sci. Total Environ. 409(12) , 2373-8, (2011) Anticoagulant rodenticides are widely used to control rodent populations but they also pose a risk of secondary poisoning in non-target predators. Studies on anticoagulant rodenticide exposure of non-target species have mainly reported on frequency of occurre... |
|
|
Resistance testing and the effectiveness of difenacoum against Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in a tyrosine139cysteine focus of anticoagulant resistance, Westphalia, Germany.
Pest Manag. Sci. 69(2) , 233-9, (2013) Anticoagulant resistance in Norway rats at foci in Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom is genetically characterised by the same single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and consequent amino acid exchange from tyrosine to cyst... |
|
|
Whole-carcass residues of the rodenticide difenacoum in anticoagulant-resistant and -susceptible rat strains (Rattus norvegicus).
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 24(2) , 318-23, (2005) The present study investigated the whole-carcass residue carried by resistant and susceptible laboratory rat strains following 5, 10, or 20 d of feeding on a diet of 25 mg difenacoum/kg bait. The mean whole-carcass residue of difenacoum was determined by high... |
|
|
HPLC determination of anticoagulant rodenticide residues in animal livers.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 56(1) , 8-15, (1996)
|
|
|
Symptom-dependent taste aversion induced by an anticoagulant rodenticide in the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus).
J. Comp. Psychol. 108(3) , 282-90, (1994) In a series of 3 experiments with different experimental paradigms, feeding patterns of laboratory rats (Rattus norvegicus) were monitored in 2-choice feeding tests after intubation with a sublethal dose of an anticoagulant rodenticide. We report for the firs... |
|
|
Intoxication with three different superwarfarin compounds in an adult woman.
Thromb. Haemost. 100(1) , 156-7, (2008)
|