anilazine
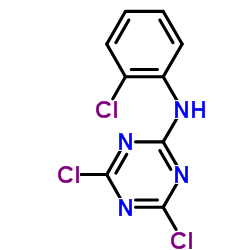
anilazine structure
|
Common Name | anilazine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 101-05-3 | Molecular Weight | 275.522 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 460.4±47.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H5Cl3N4 | Melting Point | 159 - 160ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 232.2±29.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Long-term persistence of various 14C-labeled pesticides in soils.
Environ. Pollut. 168 , 29-36, (2012) The fate of the 14C-labeled herbicides ethidimuron (ETD), methabenzthiazuron (MBT), and the fungicide anilazine (ANI) in soils was evaluated after long-term aging (9-17 years) in field based lysimeters subject to crop rotation. Analysis of residual 14C activi... |
|
|
Dry-wet cycles increase pesticide residue release from soil.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 31(9) , 1941-7, (2012) Soil drying and rewetting may alter the release and availability of aged pesticide residues in soils. A laboratory experiment was conducted to evaluate the influence of soil drying and wetting on the release of pesticide residues. Soil containing environmenta... |
|
|
Allergic contact dermatitis from a lawn care fungicide containing dyrene.
Am. J. Contact Dermatitis 8(1) , 47-8, (1997) Lawn care chemicals are frequently blamed when skin rashes occur in lawn care workers, although proof of a cause-and-effect relationship is often lacking. A lawn care worker developed severe dermatitis of the hands, arms, face, and neck shortly after his comp... |
|
|
An outbreak of contact dermatitis in farm workers.
J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 13(2 Pt 1) , 220-3, (1985) Fourteen of twenty-six migrant workers developed contact dermatitis at a single tomato-strawberry farm in Tennessee. Investigation identified one of eleven pesticides used by the farmer, 2,4-dichloro-6-(o-chloroanilino)-s-triazine anilazine; Dyrene), as the c... |
|
|
Microbial release and degradation of nonextractable anilazine residues.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(9) , 3905-10, (1999) Humic substance fractions obtained from a degraded loess soil taken from a long-term lysimeter experiment with the fungicide anilazine were incubated in aerated liquid cultures together with native soil microorganisms. Biomineralization, remobilization of [U-... |
|
|
Triazines.
Toxicology 91(1) , 59-62, (1994)
|
|
|
Comparison of gas and liquid chromatography for determination of anilazine in potatoes and tomatoes.
J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 63(6) , 1300-3, (1980) Anilazine (2,4-dichloro-6-(2-chloroanilino)-1,3,5-triazine), a triazine fungicide, is extracted from potatoes or tomatoes with acetonitrile. An aliquot of the filtered extract is partitioned between methylene chloride and water. The organic phase is concentra... |
|
|
Photoinduced addition of the fungicide anilazine to cyclohexene and methyl oleate as model compounds of plant cuticle constituents.
Chemosphere 41(9) , 1401-6, (2000) Photoreactions, initiated by sunlight irradiation, between organochlorine pesticides and olefinic compounds of plant cuticles have been postulated. Concerning the formation of bound residues, which so far have not been detectable by common analytical techniqu... |
|
|
Effect of anilazine on growth, respiration and enzyme activity of Escherichia coli.
Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Naturwiss. 136(6) , 505-8, (1981) The effect of anilazine on growth, respiration and enzyme activity of E. coli has been studied. Anilazine delays the growth of E. coli by prolonging the lag period. It inhibits glucose oxidation by 60% and succinate oxidation by 100%. It also inhibits in vitr... |
|
|
Consideration of individual susceptibility in adverse pesticide effects.
Toxicol. Lett. 107(1-3) , 131-44, (1999) The modern environmental awareness leads to the realisation that the human metabolism is stressed by a huge number of chemical substances. Generally, these background exposures, consisting predominantly from natural and partly from industrial as well as life ... |