L-Selenomethionine
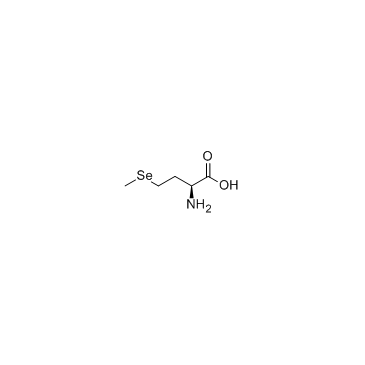
L-Selenomethionine structure
|
Common Name | L-Selenomethionine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3211-76-5 | Molecular Weight | 196.106 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 320.8±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2Se | Melting Point | 265 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 147.8±26.5 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression.
Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009) Multiple, complex molecular events characterize cancer development and progression. Deciphering the molecular networks that distinguish organ-confined disease from metastatic disease may lead to the identification of critical biomarkers for cancer invasion an... |
|
|
Structure of the Ergothioneine-Biosynthesis Amidohydrolase EgtC.
ChemBioChem. 16 , 1490-6, (2015) The ubiquitous sulfur metabolite ergothioneine is biosynthesized by oxidative attachment of a sulfur atom to the imidazole ring of Nα-trimethylhistidine. Most actinobacteria, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, use γ-glutamyl cysteine as a sulfur donor. In ... |
|
|
Antitumor activity of an enzyme prodrug therapy targeted to the breast tumor vasculature.
Cancer Invest. 31(8) , 505-10, (2013) The L-methioninase-annexin V/selenomethionine enzyme prodrug system, designed to target the tumor vasculature and release the methylselenol anticancer drug in the tumor, was tested in mice with implanted MBA-MB-231 breast tumors. This therapy was able to caus... |
|
|
Dose-Dependent Early Life Stage Toxicities in Xenopus laevis Exposed In Ovo to Selenium.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 , 13658-66, (2015) Selenium (Se) is a developmental toxicant in oviparous vertebrates. The adverse reproductive effects of Se toxicity have been predominantly investigated in fishes and birds with only a few studies focusing on amphibians. The objective of this study was to det... |
|
|
Dietary selenomethionine exposure alters swimming performance, metabolic capacity and energy homeostasis in juvenile fathead minnow.
Aquat. Toxicol. 155 , 91-100, (2014) Selenium (Se) is known to cause chronic toxicity in aquatic species. In particular, dietary exposure of fish to selenomethionine (SeMet), the primary form of Se in the diet, is of concern. Recent studies suggest that chronic exposure to elevated dietary SeMet... |
|
|
Identification of selenium-containing proteins in HEK 293 kidney cells using multiple chromatographies, LC-ICPMS and nano-LC-ESIMS.
Talanta 114 , 25-31, (2013) Our previous studies using HeLa and HEK 293 cells demonstrated that selenomethionine, SeMet, exerts more of an antagonistic effect on arsenic than other selenium species. These studies attributed the antagonistic effect of SeMet to decreased levels of reactiv... |
|
|
Selenium and selenomethionine levels in prostate cancer patients.
Cancer Detect. Prev. 28(1) , 8-16, (2004) Selenium (Se) and selenomethionine (Se-Met) have been identified as potential chemopreventive agents of prostate cancer. Using an assay for the speciation (separation and identification) and quantification of selenoamino acids, Se-Met was profiled in serum an... |
|
|
Urinary unconjugated 5 alpha-androstane-3 alpha, 17 beta-diol in patients with prostatic tumours.
Urol. Res. 10(2) , 81-4, (1982) A sensitive and reliable radioimmunoassay (RIA) for urinary unconjugated 5 alpha-androstane-3 alpha, 17 beta-diol is described. The mean overall recovery of unconjugated 5 alpha-androstane-3 alpha, 17 beta-diol was found to be 57.4%. The sensitivity of the as... |
|
|
Plasma carotenoids, retinol, and tocopherols and the risk of prostate cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study.
Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 86(3) , 672-81, (2007) Previous studies suggest that high plasma concentrations of carotenoids, retinol, or tocopherols may reduce the risk of prostate cancer.We aimed to examine the associations between plasma concentrations of 7 carotenoids, retinol, alpha-tocopherol, and gamma-t... |