(-)-Gallocatechin
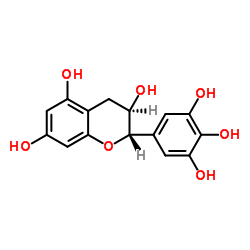
(-)-Gallocatechin structure
|
Common Name | (-)-Gallocatechin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3371-27-5 | Molecular Weight | 306.267 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 685.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H14O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 368.5±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Identification and quantification of phytochemicals in nutraceutical products from green tea by UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS.
Food Chem. 173 , 607-18, (2014) A method has been developed and validated for the simultaneous detection and quantification of phytochemicals in nutraceutical products obtained from green tea. For that purpose, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to single-stage Orbitrap hi... |
|
|
An efficient and economical MTT assay for determining the antioxidant activity of plant natural product extracts and pure compounds.
J. Nat. Prod. 73 , 1193-5, (2010) Antioxidants scavenge free radicals, singlet oxygen, and electrons in cellular redox reactions. The yellow MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] is reduced to a purple formazan by mitochondrial enzymes. NADPH is the basis of esta... |
|
|
Radical-scavenging activity of dietary phytophenols in combination with co-antioxidants using the induction period method.
Molecules 16(12) , 10457-70, (2011) The radical-scavenging activity of dietary phytophenols has been investigated by many researches due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer property but the radical-scavenging effect of 2-phytophenol and the phytophenol:co-antioxidants, vitami... |
|
|
Development of a fast extraction method and optimization of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the analysis of phenolic compounds in lentil seed coats.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 969 , 149-61, (2014) A systematic set of optimization experiments was conducted to design an efficient extraction and analysis protocol for screening six different sub-classes of phenolic compounds in the seed coat of various lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) genotypes. Different co... |
|
|
Development and validation of UHPLC-MS/MS method for determination of eight naturally occurring catechin derivatives in various tea samples and the role of matrix effects.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 114 , 62-70, (2015) A complete analytical procedure combining optimized tea infusion preparation and validated UHPLC-MS/MS method was developed for routine quantification of eight naturally occurring catechin derivatives in various tea samples. The preparation of tea infusions w... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of rat intestinal bacteria involved in biotransformation of (-)-epigallocatechin.
Arch. Microbiol. 196(10) , 681-95, (2014) Two intestinal bacterial strains MT4s-5 and MT42 involved in the degradation of (-)-epigallocatechin (EGC) were isolated from rat feces. Strain MT4s-5 was tentatively identified as Adlercreutzia equolifaciens. This strain converted EGC into not only 1-(3, 4, ... |
|
|
Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Polyphenols in a Traditional Japanese Medicine, Jumihaidokuto, Which Suppresses Propionibacterium acnes-Induced Dermatitis in Rats.
Molecules 20 , 18031-46, (2015) Most orally administered polyphenols are metabolized, with very little absorbed as aglycones and/or unchanged forms. Metabolic and pharmacokinetic studies are therefore necessary to understand the pharmacological mechanisms of polyphenols. Jumihaidokuto (JHT)... |
|
|
Green tea catechins increase the force of contraction in isolated guinea pig atrial muscle preparations by increasing the amplitude of intracellular Ca2+ concentration.
J. Vet. Med. Sci. 74 , 1603-1608, (2012) It has been reported that green tea catechins enhance the force of contraction of isolated heart muscle preparations. However, it remains controversial whether or not the increase in force of contraction is related to an increase in the intracellular Ca(2+) c... |
|
|
Polyphenol content of plasma and litter after the oral administration of green tea and tea polyphenols in chickens.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(7) , 1619-27, (2012) Metabolic profiles of broiler chickens were examined after the ingestion of green tea, tea polyphenols, and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Solid-phase extraction of serum and litters yielded free catechins and their metabolites, which were then identi... |
|
|
A new norisoprenoid and other compounds from Fuzhuan brick tea.
Molecules 17(3) , 3539-46, (2012) Fuzhuan brick tea, a kind of dark tea consumed mainly in the border regions of Southwestern and Northwestern China since the 1860s, is produced from the leaves of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis by microbial fermentation. From this special fermented tea, a ne... |