EHNA.HCl
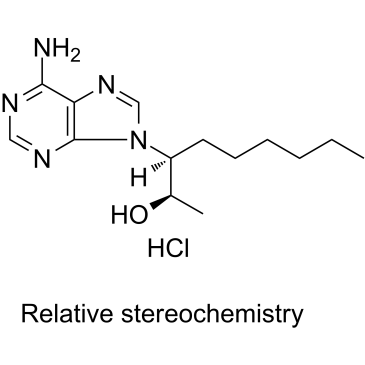
EHNA.HCl structure
|
Common Name | EHNA.HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58337-38-5 | Molecular Weight | 313.826 | |
| Density | 1.27g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 478.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H24ClN5O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 243ºC | |
|
Regulation of autophagic flux by dynein-mediated autophagosomes trafficking in mouse coronary arterial myocytes
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1833(12) , 3228-36, (2013) Autophagic flux is an important process during autophagy maturation in coronary arterial myocytes (CAMs). Here, we defined the role and molecular mechanism of the motor protein dynein in the regulation of autophagic flux in CAMs. In mouse CAMs, dynein protein... |
|
|
Adenosine activation of A(2B) receptor(s) is essential for stimulated epithelial ciliary motility and clearance.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 301(2) , L171-80, (2011) Mucociliary clearance, vital to lung clearance, is dependent on cilia beat frequency (CBF), coordination of cilia, and the maintenance of periciliary fluid. Adenosine, the metabolic breakdown product of ATP, is an important modulator of ciliary motility. Howe... |
|
|
Adenosine accelerates the healing of diabetic ischemic ulcers by improving autophagy of endothelial progenitor cells grown on a biomaterial.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 11594, (2015) Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) seeded on biomaterials can effectively promote diabetic ischemic wound healing. However, the function of transplanted EPCs is negatively affected by a high-glucose and ischemic microenvironment. Our experiments showed that ... |
|
|
Microtubules are required for efficient epithelial tight junction homeostasis and restoration.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 307(3) , C245-54, (2014) Epithelial tight junctions are critical for creating a barrier yet allowing paracellular transport. Although it is well established that the actin cytoskeleton is critical for preserving the dynamic organization of the tight junction and maintaining normal ti... |
|
|
Adenosine-mediated cardiovascular toxicity in amitriptyline-poisoned rats.
Drug Chem. Toxicol. 35(4) , 423-31, (2012) We investigated the contribution of endogenous adenosine to amitriptyline-induced cardiovascular toxicity in rats. A control group of rats was pretreated with intraperitoneal (i.p.) 5% dextrose and received intravenous 0.94 mg/kg/min of amitriptyline for 60 m... |
|
|
On-pump inhibition of es-ENT1 nucleoside transporter and adenosine deaminase during aortic crossclamping entraps intracellular adenosine and protects against reperfusion injury: role of adenosine A1 receptor.
J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 144(1) , 243-9, (2012) The inhibition of adenosine deaminase with erythro-9 (2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)-adenine (EHNA) and the es-ENT1 transporter with p-nitro-benzylthioinosine (NBMPR), entraps myocardial intracellular adenosine during on-pump warm aortic crossclamping, leading to a compl... |
|
|
Hot shot induction and reperfusion with a specific blocker of the es-ENT1 nucleoside transporter before and after hypothermic cardioplegia abolishes myocardial stunning in acutely ischemic hearts despite metabolic derangement: hot shot drug delivery before hypothermic cardioplegia.
J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 146(4) , 961-970.e3, (2013) Simultaneous inhibition of the cardiac equilibrative-p-nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)-sensitive (es) type of the equilibrative nucleoside transport 1 (ENT1) nucleoside transporter, with NBMPR, and adenosine deaminase, with erythro-9-[2-hydroxy-3-nonyl]adenine... |
|
|
Measurement of deoxyinosine adduct: Can it be a reliable tool to assess oxidative or nitrosative DNA damage?
Toxicol. Lett. 214(2) , 226-33, (2012) Adenosine deaminases (ADA) are key enzymes that deaminate adenosine (A) or deoxyadenosine (dA) and produce inosine or deoxyinosine (dI), respectively. While ADA only deaminates free dA, reactive nitrogen species (RNS) or reactive oxygen species (ROS) deaminat... |
|
|
Inhibition of ATP release from erythrocytes: a role for EPACs and PKC.
Microcirculation 18(2) , 128-35, (2011) Here we demonstrate that, in human erythrocytes, increases in cAMP that are not localized to a specific receptor-mediated signaling pathway for ATP release can activate effector proteins resulting in inhibition of ATP release. Specifically we sought to establ... |
|
|
A novel mouse model for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP): role of impaired adenosine clearance.
Epilepsia 51(3) , 465-8, (2010) Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is a significant cause of mortality in people with epilepsy. Two postulated causes for SUDEP, cardiac and respiratory depression, can both be explained by overstimulation of adenosine receptors. We hypothesized that... |