DL-Homocysteine
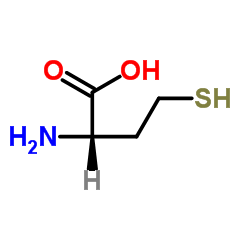
DL-Homocysteine structure
|
Common Name | DL-Homocysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6027-13-0 | Molecular Weight | 135.185 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 299.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO2S | Melting Point | 231 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 135.0±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Biomarkers of one-carbon metabolism are associated with biomarkers of inflammation in women.
J. Nutr. 144(5) , 714-21, (2014) Folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism is essential for DNA synthesis, repair, and methylation. Perturbations in one-carbon metabolism have been implicated in increased risk of some cancers and may also affect inflammatory processes. We investigated these inte... |
|
|
Abstracts of the 9th International Conference On Homocysteine and One-Carbon Metabolism - HCY2013. Dublin, Ireland. September 8-12, 2013.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 36 Suppl 1 , S1-54, (2013)
|
|
|
Derivation and validation of homocysteine score in u.s. Men and women.
J. Nutr. 145(1) , 96-104, (2015) One-carbon metabolism, which is crucial in DNA synthesis and genomic stability, is an interrelated network of biochemical reactions involved in several dietary and lifestyle factors. The development of the homocysteine score using these factors may be useful ... |
|
|
Hyperhomocysteinemia and assessment of its associated factors in renal transplant recipients: a single-center study in northern Iran.
Transplantation 98(1) , 66-71, (2014) Hyperhomocysteinemia (hyperHcy) is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis, which is currently a major cause of death in renal transplant patients (RTRs). The aim of this study was to determine the associated factors of hyperHcy in RTRs in northern Iran.... |
|
|
An integrated metabolomics workflow for the quantification of sulfur pathway intermediates employing thiol protection with N-ethyl maleimide and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.
Analyst 140 , 7687-95, (2015) The sulfur metabolic pathway is involved in basic modes of cellular metabolism, including methylation, cell division, respiratory oscillations and stress responses. Hence, the implicated high reactivity of the sulfur pathway intermediates entails challenges f... |
|
|
Homocysteine Triggers Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages through Inhibiting CSE-H2S Signaling via DNA Hypermethylation of CSE Promoter.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 12560-77, (2015) Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) is an independent risk factor of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. Unfortunately, Hcy-lowering strategies were found to have limited effects in reducing cardiovascular events. The underlying mechanisms remain uncle... |
|
|
Maternal first-trimester diet and childhood bone mass: the Generation R Study.
Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 98(1) , 224-32, (2013) Maternal diet during pregnancy has been suggested to influence bone health in later life.We assessed the association of maternal first-trimester dietary intake during pregnancy with childhood bone mass.In a prospective cohort study in 2819 mothers and their c... |
|
|
Structural Analysis of a Fungal Methionine Synthase with Substrates and Inhibitors
J. Mol. Biol. 426(8) , 1839-47, (2014) The cobalamin-independent methionine synthase from Candida albicans, known as Met6p, is a 90-kDa enzyme that consists of two (βα)8 barrels. The active site is located between the two domains and has binding sites for a zinc ion and substrates l-homocysteine a... |
|
|
Body composition in patients with classical homocystinuria: body mass relates to homocysteine and choline metabolism.
Gene 546(2) , 443-7, (2014) Classical homocystinuria is a rare genetic disease caused by cystathionine β-synthase deficiency, resulting in homocysteine accumulation. Growing evidence suggests that reduced fat mass in patients with classical homocystinuria may be associated with alterati... |
|
|
DNA methylation potential: dietary intake and blood concentrations of one-carbon metabolites and cofactors in rural African women.
Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 97(6) , 1217-27, (2013) Animal models show that periconceptional supplementation with folic acid, vitamin B-12, choline, and betaine can induce differences in offspring phenotype mediated by epigenetic changes in DNA. In humans, altered DNA methylation patterns have been observed in... |