6-HYDROXYDOPAMINE HYDROBROMIDE
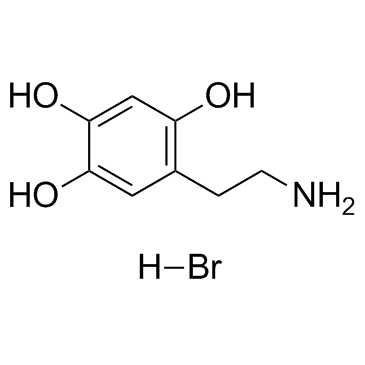
6-HYDROXYDOPAMINE HYDROBROMIDE structure
|
Common Name | 6-HYDROXYDOPAMINE HYDROBROMIDE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 636-00-0 | Molecular Weight | 250.090 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 406ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12BrNO3 | Melting Point | 216-220 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 199.3ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil in the striatal 6-hydroxydopamine lesion mouse model of Parkinson disease.
J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 73(8) , 770-9, (2014) Chronic degeneration of nigrostriatal projections, followed by nigral dopaminergic cell death, is a key feature of Parkinson disease (PD). This study examines the neuroprotective potential of the rho kinase inhibitor fasudil in the 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) ... |
|
|
Curcumin I mediates neuroprotective effect through attenuation of quinoprotein formation, p-p38 MAPK expression, and caspase-3 activation in 6-hydroxydopamine treated SH-SY5Y cells.
Phytother Res. 28(4) , 611-6, (2014) 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) selectively enters dopaminergic neurons and undergoes auto-oxidation resulting in the generation of reactive oxygen species and dopamine quinones, subsequently leading to apoptosis. This mechanism mimics the pathogenesis of Parkinso... |
|
|
Ameliorating effects of curcumin on 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic denervation, glial response, and SOD1 reduction in the striatum of hemiparkinsonian mice.
Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 17(10) , 1360-8, (2013) Inflammation and oxidative stress are believed to contribute to neuronal degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic (DA) pathway in Parkinson's disease. Curcumin, a component of the yellow curry spice, has been reported possessing anti-inflammatory and an... |
|
|
Effects of squalene/squalane on dopamine levels, antioxidant enzyme activity, and fatty acid composition in the striatum of Parkinson's disease mouse model.
J. Oleo Sci. 62(1) , 21-8, (2013) Active oxygen has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD); therefore, antioxidants have attracted attention as a potential way to prevent this disease. Squalene, a natural triterpene and an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholester... |
|
|
Optogenetic inactivation of the subthalamic nucleus improves forelimb akinesia in a rat model of Parkinson disease.
Neurosurgery 74(5) , 533-40; discussion 540-1, (2014) The inhibition of neuronal activity by electrical deep brain stimulation is one of the mechanisms explaining the therapeutic effects in patients with Parkinson disease (PD) but cannot specifically activate or inactivate different types of neurons. Recently, a... |
|
|
Side effect profile of 5-HT treatments for Parkinson's disease and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in rats.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(1) , 119-30, (2014) Treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) with L-DOPA eventually causes abnormal involuntary movements known as dyskinesias in most patients. Dyskinesia can be reduced using compounds that act as direct or indirect agonists of the 5-HT1 A receptor, but these drug... |
|
|
An in vivo microdialysis study of FLZ penetration through the blood-brain barrier in normal and 6-hydroxydopamine induced Parkinson's disease model rats.
Biomed Res. Int. 2014 , 850493, (2014) FLZ (N-[2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-2-(2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-phenyl)-acrylamide) is a novel synthetic squamosamide derivative and a potential anti-Parkinson's disease (PD) agent. The objective of the present study was to investigate the... |
|
|
NRF2 Regulates PINK1 Expression under Oxidative Stress Conditions.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0142438, (2015) Mutations of the PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) gene are a cause of autosomal recessive forms of Parkinson's disease. Recent studies have revealed that PINK1 is an essential factor for controlling mitochondrial quality, and that it protects cells from... |
|
|
Behavioral characterization of the 6-hydroxidopamine model of Parkinson's disease and pharmacological rescuing of non-motor deficits.
Molecular Neurodegeneration 8 , 14, (2013) Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative condition that is characterized by motor symptoms as a result of dopaminergic degeneration, particularly in the mesostriatal pathway. However, in recent years, a greater number of clinical studies have f... |
|
|
Decreased SIRT2 activity leads to altered microtubule dynamics in oxidatively-stressed neuronal cells: implications for Parkinson's disease.
Exp. Neurol. 257 , 170-81, (2014) The microtubule (MT) system is important for many aspects of neuronal function, including motility, differentiation, and cargo trafficking. Parkinson's disease (PD) is associated with increased oxidative stress and alterations in the integrity of the axodendr... |