trans-3-Hydroxycinnamic acid
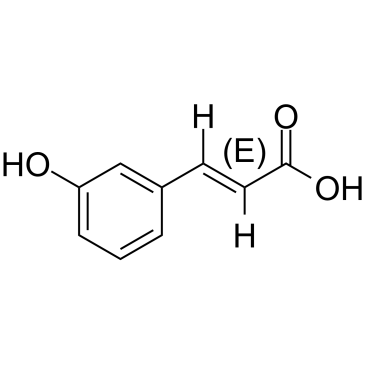
trans-3-Hydroxycinnamic acid structure
|
Common Name | trans-3-Hydroxycinnamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 14755-02-3 | Molecular Weight | 164.158 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 373.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O3 | Melting Point | 193-195 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 193.7±19.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only a few antimicrobial agents left that can be used against MD... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
Protective Effects of Catechin against Monosodium Urate-Induced Inflammation through the Modulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 7343-52, (2015) Gouty inflammation results from the stimulation of monosodium urate (MSU). Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) secretion is the primary clinical manifestation of MSU attack, and MSU activates IL-1β through a nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor containi... |
|
|
The tomato sauce making process affects the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of tomato phenolics: a pharmacokinetic study.
Food Chem. 173 , 864-72, (2014) Tomato sauce is the most commonly consumed processed tomato product worldwide, but very little is known about how the manufacturing process may affect the phenolic composition and bioavailability after consumption. In a prospective randomised, cross-over inte... |
|
|
Development of a targeted method for twenty-three metabolites related to polyphenol gut microbial metabolism in biological samples, using SPE and UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS.
Talanta 128 , 221-30, (2014) An increasing number of studies have concerned the profiling of polyphenol microbial metabolites, especially in urine or plasma, but only a few have regarded their accurate quantification. This study reports on a new ultra-performance liquid chromatography ta... |
|
|
A chemical screening approach reveals that indole fluorescence is quenched by pre-fibrillar but not fibrillar amyloid-beta.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 4952-7, (2009) Aggregated amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide is implicated in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. In vitro and in vivo, these aggregates are found in a variety of morphologies, including globular oligomers and linear fibrils, which possess distinct biological ac... |
|
|
Structure-activity relationships of 1'S-1'-acetoxychavicol acetate for inhibitory effect on NO production in lipopolysaccharide-activated mouse peritoneal macrophages.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15 , 1949-53, (2005) 1'S-1'-Acetoxychavicol acetate from the rhizomes of Alpinia galanga inhibited nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide-activated mouse peritoneal macrophages with an IC(50) value of 2.3 microM. To clarify the structure-activity relationship of 1'S-1... |
|
|
Structure-activity relationships of trans-substituted-propenoic acid derivatives on the nicotinic acid receptor HCA2 (GPR109A).
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 2736-9, (2011) Nicotinic acid (niacin) has been used for decades as an antidyslipidemic drug in man. Its main target is the hydroxy-carboxylic acid receptor HCA2 (GPR109A), a G protein-coupled receptor. Other acids and esters such as methyl fumarate also interact with the r... |
|
|
Contribution of cinnamic acid analogues in rosmarinic acid to inhibition of snake venom induced hemorrhage.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 2392-6, (2011) In our previous paper, we reported that rosmarinic acid (1) of Argusia argentea could neutralize snake venom induced hemorrhagic action. Rosmarinic acid (1) consists of two phenylpropanoids: caffeic acid (2) and 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)lactic acid (3). In this... |
|
|
Fate of microbial metabolites of dietary polyphenols in rats: is the brain their target destination?
ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6 , 1341-52, (2015) Different polyphenol compounds are ingested when consuming a serving of fruits rich in polyphenols, spanning from one-phenol hydroxybenzoic acid to more complex polymeric compounds. Only a minor quantity of the polyphenols (5-10%) is absorbed. The remainder r... |