Picrotoxin
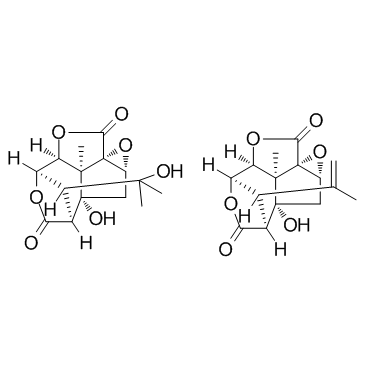
Picrotoxin structure
|
Common Name | Picrotoxin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 124-87-8 | Molecular Weight | 301.29 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H18O7.C15H16O6 | Melting Point | 203 ℃(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Frequency-dependent, cell type-divergent signaling in the hippocamposeptal projection.
J. Neurosci. 34(35) , 11769-80, (2014) Hippocampal oscillations are critical for information processing, and are strongly influenced by inputs from the medial septum. Hippocamposeptal neurons provide direct inhibitory feedback from the hippocampus onto septal cells, and are therefore likely to als... |
|
|
Parallel ON and OFF cone bipolar inputs establish spatially coextensive receptive field structure of blue-yellow ganglion cells in primate retina.
J. Mol. Endocrinol. 29 , 8372-87, (2009) In the primate retina the small bistratified, "blue-yellow" color-opponent ganglion cell receives parallel ON-depolarizing and OFF-hyperpolarizing inputs from short (S)-wavelength sensitive and combined long (L)- and middle (M)-wavelength sensitive cone photo... |
|
|
Modifications of diflunisal and meclofenamate carboxyl groups affect their allosteric effects on GABAA receptor ligand binding.
Neurochem. Res. 39(7) , 1183-91, (2014) Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors (GABAAR) are allosterically modulated by the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs diflunisal and fenamates. The carboxyl group of these compounds is charged at physiological pH and therefore penetration of the compound... |
|
|
TRPV1 channels control synaptic plasticity in the developing superior colliculus.
J. Physiol. 587(Pt 11) , 2521-35, (2009) Long-term depression (LTD) in the rodent superior colliculus (SC) is regarded as a model of synaptic refinement because it can be induced during development but not in adults. We investigated the role of transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 (TRPV1) c... |
|
|
Homeostatic regulation of h-conductance controls intrinsic excitability and stabilizes the threshold for synaptic modification in CA1 neurons.
J. Physiol. 593 , 4855-69, (2015) We determined the contribution of the hyperpolarization-activated cationic (h) current (Ih ) to the homeostatic regulation of CA1 pyramidal cells in vitro using chronic treatments (48 h) that either increase (picrotoxin) or decrease (kynurenate) neuronal acti... |
|
|
A Positive Allosteric Modulator of the Adenosine A1 Receptor Selectively Inhibits Primary Afferent Synaptic Transmission in a Neuropathic Pain Model.
Mol. Pharmacol. 88 , 460-8, (2015) In the spinal cord and periphery, adenosine inhibits neuronal activity through activation of the adenosine A1 receptor (A1R), resulting in antinociception and highlighting the potential of therapeutically targeting the receptor in the treatment of neuropathic... |
|
|
Seizure reduction through interneuron-mediated entrainment using low frequency optical stimulation.
Exp. Neurol. 269 , 120-32, (2015) Low frequency electrical stimulation (LFS) can reduce neural excitability and suppress seizures in animals and patients with epilepsy. However the therapeutic outcome could benefit from the determination of the cell types involved in seizure suppression. We u... |
|
|
Autism-Associated Insertion Mutation (InsG) of Shank3 Exon 21 Causes Impaired Synaptic Transmission and Behavioral Deficits.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 9648-65, (2015) SHANK3 (also known as PROSAP2) is a postsynaptic scaffolding protein at excitatory synapses in which mutations and deletions have been implicated in patients with idiopathic autism, Phelan-McDermid (aka 22q13 microdeletion) syndrome, and other neuropsychiatri... |
|
|
Glucose sensing by GABAergic neurons in the mouse nucleus tractus solitarii.
J. Neurophysiol. 114 , 999-1007, (2015) Changes in blood glucose concentration alter autonomic function in a manner consistent with altered neural activity in brain regions controlling digestive processes, including neurons in the brain stem nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS), which process viscerosen... |
|
|
Intrinsic excitability varies by sex in prepubertal striatal medium spiny neurons.
J. Neurophysiol. 113(3) , 720-9, (2015) Sex differences in neuron electrophysiological properties were traditionally associated with brain regions directly involved in reproduction in adult, postpubertal animals. There is growing acknowledgement that sex differences can exist in other developmental... |