Resiniferatoxin
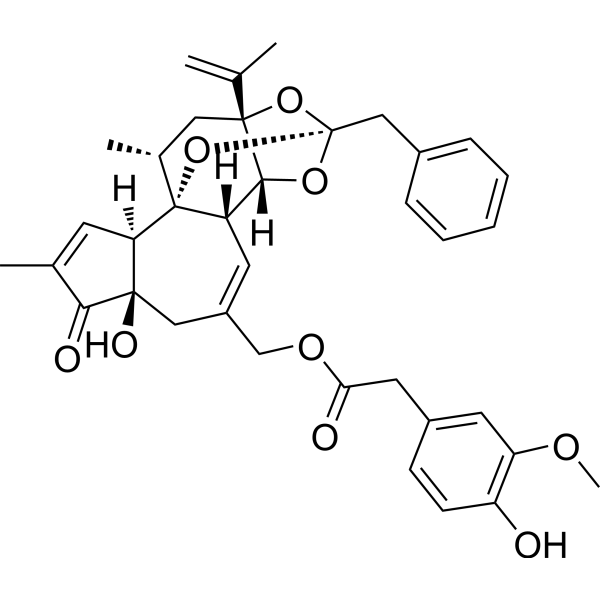
Resiniferatoxin structure
|
Common Name | Resiniferatoxin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 57444-62-9 | Molecular Weight | 628.71 | |
| Density | 1.35g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 768.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C37H40O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 240.3ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Activation of the TRPV1 cation channel contributes to stress-induced astrocyte migration.
Glia 62(9) , 1435-51, (2014) Astrocytes provide metabolic, structural, and synaptic support to neurons in normal physiology and also contribute widely to pathogenic processes in response to stress or injury. Reactive astrocytes can undergo cytoskeletal reorganization and increase migrati... |
|
|
TRPM5-dependent amiloride- and benzamil-insensitive NaCl chorda tympani taste nerve response.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 305(1) , G106-17, (2013) Transient receptor potential (TRP) subfamily M member 5 (TRPM5) cation channel is involved in sensing sweet, bitter, umami, and fat taste stimuli, complex-tasting divalent salts, and temperature-induced changes in sweet taste. To investigate if the amiloride-... |
|
|
Inhibition by capsaicin and its related vanilloids of compound action potentials in frog sciatic nerves.
Life Sci. 92(6-7) , 368-78, (2013) Although capsaicin not only activates transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) channels but also inhibits nerve conduction, the latter action has not yet been fully examined. The purpose of the present study was to know whether various vanilloids have... |
|
|
Pan-CC chemokine neutralization restricts splenocyte egress and reduces inflammation in a model of arthritis.
J. Immunol. 185 , 2544-54, (2010) Chemokines are key regulators of leukocyte trafficking and play a crucial role under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions. Because chemokines are involved in multiple pathologies, they represent an attractive class of therapeutic targets. However, because ... |
|
|
Identification of the plant steroid α-spinasterol as a novel transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 antagonist with antinociceptive properties.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 343(2) , 258-69, (2012) The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor is relevant to the perception of noxious information and has been studied as a therapeutic target for the development of new analgesics. The goal of this study was to perform in vivo and in vitro s... |
|
|
Genesis of anxiety, depression, and ongoing abdominal discomfort in ulcerative colitis-like colon inflammation.
Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 308(1) , R18-27, (2015) Psychological disorders are prevalent in patients with inflammatory bowel disease; the underlying mechanisms remain unknown. We tested the hypothesis that ulcerative colitis-like inflammation induced by dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) exacerbates the ongoing spo... |
|
|
"Chemical-pain sensor" based on nanovesicle-carbon nanotube hybrid structures.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 49 , 86-91, (2013) We developed a "chemical-pain sensor" that could recognize chemical pain stimuli such as capsaicin and resiniferatoxin just like mammalian chemical pain sensory systems. Here, we first prepared nanovesicles containing rat pain sensory receptor, rat transient ... |
|
|
Cardiac sympathetic afferent denervation attenuates cardiac remodeling and improves cardiovascular dysfunction in rats with heart failure.
Hypertension 64(4) , 745-55, (2014) The enhanced cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex (CSAR) contributes to the exaggerated sympathoexcitation in chronic heart failure (CHF). Increased sympathoexcitation is positively related to mortality in patients with CHF. However, the potential beneficial e... |
|
|
Opioid withdrawal increases transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 activity in a protein kinase A-dependent manner.
Pain 154(4) , 598-608, (2013) Hyperalgesia is a cardinal symptom of opioid withdrawal. The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) is a ligand-gated ion channel expressed on sensory neurons responding to noxious heat, protons, and chemical stimuli such as capsaicin. TRPV1 can be ... |
|
|
Glycine transporter type 2 (GlyT2) inhibitor ameliorates bladder overactivity and nociceptive behavior in rats.
Eur. Urol. 62(4) , 704-12, (2012) Glycine is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord, the concentration of which is regulated by two types of glycine transporters (GlyTs): GlyT1 and GlyT2. We hypothesized that the inhibition of GlyTs could ameliorate bladder overactivity and/or... |