Anandamide
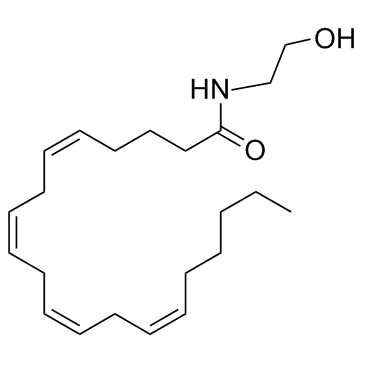
Anandamide structure
|
Common Name | Anandamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94421-68-8 | Molecular Weight | 347.535 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 522.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H37NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 269.7±30.1 °C | |
|
Gastric bypass in morbid obese patients is associated with reduction in adipose tissue inflammation via N-oleoylethanolamide (OEA)-mediated pathways.
Thromb. Haemost. 113(4) , 838-50, (2015) Paradoxically, morbid obesity was suggested to protect from cardiovascular co-morbidities as compared to overweight/obese patients. We hypothesise that this paradox could be inferred to modulation of the "endocannabinoid" system on systemic and subcutaneous a... |
|
|
On the effects of CP 55-940 and other cannabinoid receptor agonists in C6 and U373 cell lines.
Toxicol. In Vitro 29 , 1941-51, (2015) Cannabinoid receptor (CBs) agonists affect the growth of tumor cells via activation of deadly cascades. The spectrum of action of these agents and the precise role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) on oncogenic processes remain elusive. Herein we compared t... |
|
|
Endocannabinoids regulate the activity of astrocytic hemichannels and the microglial response against an injury: In vivo studies.
Neurobiol. Dis. 79 , 41-50, (2015) Anandamide (AEA) is an endocannabinoid (EC) that modulates multiple functions in the CNS and that is released in areas of injury, exerting putative neuroprotective actions. In the present study, we have used intravital microscopy to analyze the role of the EC... |
|
|
The human serum metabolome.
PLoS ONE 6(2) , e16957, (2011) Continuing improvements in analytical technology along with an increased interest in performing comprehensive, quantitative metabolic profiling, is leading to increased interest pressures within the metabolomics community to develop centralized metabolite ref... |
|
|
Effects of synthetic alkamides on Arabidopsis fatty acid amide hydrolase activity and plant development.
Phytochemistry 110 , 58-71, (2015) Alkamides and N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) are bioactive, amide-linked lipids that influence plant development. Alkamides are restricted to several families of higher plants and some fungi, whereas NAEs are widespread signaling molecules in both plants and anim... |
|
|
Correlating FAAH and anandamide cellular uptake inhibition using N-alkylcarbamate inhibitors: from ultrapotent to hyperpotent.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 92(4) , 669-89, (2014) Besides the suggested role of a putative endocannabinoid membrane transporter mediating the cellular uptake of the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA), this process is intrinsically coupled to AEA degradation by the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Differentia... |
|
|
A simple method for simultaneous determination of N-arachidonoylethanolamine, N-oleoylethanolamine, N-palmitoylethanolamine and 2-arachidonoylglycerol in human cells.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407(6) , 1781-7, (2015) The endocannabinoid system has been considered as a target for pharmacological intervention. Accordingly, inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), a degrading enzyme of the endocannabinoids N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide; AEA) and 2-arachidono... |
|
|
Inhibition of anandamide hydrolysis attenuates nociceptor sensitization in a murine model of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
J. Neurophysiol. 113(5) , 1501-10, (2015) Painful neuropathy frequently develops as a consequence of commonly used chemotherapy agents for cancer treatment and is often a dose-limiting side effect. Currently available analgesic treatments are often ineffective on pain induced by neurotoxicity. Althou... |
|
|
Effects of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Inhibitors in Non-Human Primate Models of Nicotine Reward and Relapse.
Neuropsychopharmacology 40 , 2185-97, (2015) Inhibition of the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) counteracts reward-related effects of nicotine in rats, but it has not been tested for this purpose in non-human primates. Therefore, we studied the effects of the first- and second-generation O-arylc... |
|
|
Increased tonic cannabinoid CB1R activity and brain region-specific desensitization of CB1R Gi/o signaling axis in mice with global genetic knockout of monoacylglycerol lipase.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 77 , 180-8, (2015) In mammalian brain, monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) is the primary enzyme responsible for terminating signaling function of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). Previous in vivo studies with mice indicate that both genetic and chronic pharmacolog... |