AM404
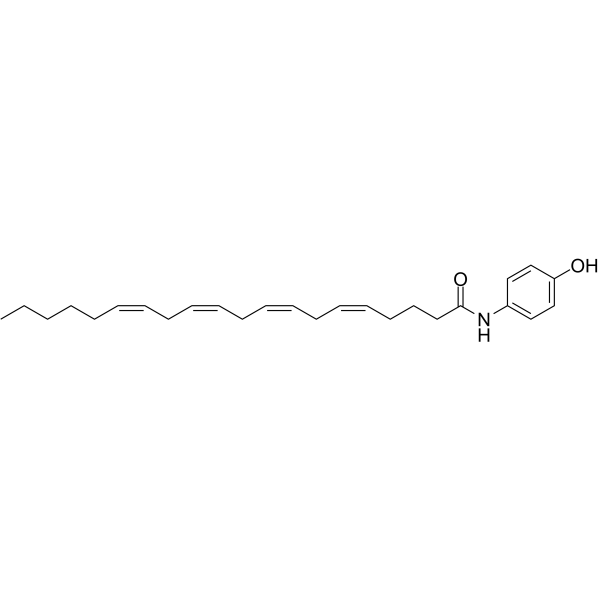
AM404 structure
|
Common Name | AM404 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 183718-77-6 | Molecular Weight | 395.578 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 579.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H37NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 304.2±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia.
Transl. Psychiatry 2 , e94, (2012) Cannabidiol is a component of marijuana that does not activate cannabinoid receptors, but moderately inhibits the degradation of the endocannabinoid anandamide. We previously reported that an elevation of anandamide levels in cerebrospinal fluid inversely cor... |
|
|
The anandamide transport inhibitor AM404 reduces the rewarding effects of nicotine and nicotine-induced dopamine elevations in the nucleus accumbens shell in rats.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 165(8) , 2539-48, (2012) The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 can reverse the abuse-related behavioural and neurochemical effects of nicotine in rats. Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors block the degradation (and thereby magnify and prolong the actions) of the endocanna... |
|
|
Elevated circulating levels of anandamide after administration of the transport inhibitor, AM404.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 408(2) , 161-8, (2000) The biological actions of the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide are terminated by carrier-mediated transport into neurons and astrocytes, followed by enzymatic hydrolysis. Anandamide transport is inhibited by the compound N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)arachidonylamide (... |
|
|
Functional role of high-affinity anandamide transport, as revealed by selective inhibition.
Science 277 , 1094-1097, (1997) Anandamide, an endogenous ligand for central cannabinoid receptors, is released from neurons on depolarization and rapidly inactivated. Anandamide inactivation is not completely understood, but it may occur by transport into cells or by enzymatic hydrolysis. ... |