prothioconazole
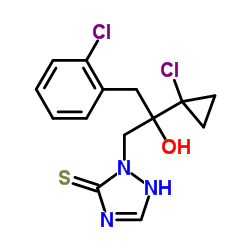
prothioconazole structure
|
Common Name | prothioconazole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 178928-70-6 | Molecular Weight | 344.259 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 486.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H15Cl2N3OS | Melting Point | 139.1-144.5° | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 248.2±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
High-performance liquid chromatographic separations of stereoisomers of chiral basic agrochemicals with polysaccharide-based chiral columns and polar organic mobile phases.
J. Sep. Sci. 38 , 4173-9, (2016) The separation of the stereoisomers of 23 chiral basic agrochemicals was studied on six different polysaccharide-based chiral columns in high-performance liquid chromatography with various polar organic mobile phases. Along with the successful separation of a... |
|
|
Triazole fungicides can induce cross-resistance to medical triazoles in Aspergillus fumigatus.
PLoS ONE 7(3) , e31801, (2012) Azoles play an important role in the management of Aspergillus diseases. Azole resistance is an emerging global problem in Aspergillus fumigatus, and may develop through patient therapy. In addition, an environmental route of resistance development has been s... |
|
|
Exposure reduction of seed treatments through dehusking behaviour of the wood mouse (Apodemus sylvaticus).
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 18 , 31-7, (2011) Seed treatments are widely used on cereals and other annual crops throughout Europe. Most of the formulated pesticide is found on the outside of the seed, the husk. Risk assessments of seed treatments are especially needed for granivorous mice living in the a... |
|
|
Identification of ABC transporter genes of Fusarium graminearum with roles in azole tolerance and/or virulence.
PLoS ONE 8 , e79042, (2013) Fusarium graminearum is a plant pathogen infecting several important cereals, resulting in substantial yield losses and mycotoxin contamination of the grain. Triazole fungicides are used to control diseases caused by this fungus on a worldwide scale. Our prev... |