Dichlofluanid
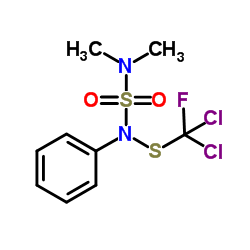
Dichlofluanid structure
|
Common Name | Dichlofluanid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1085-98-9 | Molecular Weight | 333.230 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 336.8±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11Cl2FN2O2S2 | Melting Point | 105.6ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 157.5±30.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Probabilistic risk assessment of common booster biocides in surface waters of the harbours of Gran Canaria (Spain)
Mar. Pollut. Bull. 62(5) , 985-91, (2011) Research highlights ► Monitoring of booster biocides levels in water samples of six different harbours. ► Greater levels of Irgarol 1051 and diuron were found in marinas than others harbours. ► Temporal evolution of booster biocides levels showed no evident f... |
|
|
Toxicity evaluation of single and mixed antifouling biocides using the Strongylocentrotus intermedius sea urchin embryo test.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 30(3) , 692-703, (2011) The present study evaluated the single and mixed toxicities of commonly used antifouling biocides (copper pyrithione, Sea nine 211, dichlofluanid, tolylfluanid, and Irgarol 1051) on the early embryogenesis of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Their t... |
|
|
Applicability of microwave-assisted extraction combined with LC-MS/MS in the evaluation of booster biocide levels in harbour sediments.
Chemosphere 82(1) , 96-102, (2011) A new sample treatment method for the determination of four common booster biocides (Diuron, TCMTB, Irgarol 1051 and Dichlofluanid) in harbour sediment samples has been developed that uses liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) after microw... |
|
|
Study on the new antifouling compounds in Korean coasts.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 85(5) , 538-43, (2010) After prohibition of use of organic tin compounds, new antifouling agents have been used as substitute paints. In 2009, this lab re-conducted the same research from 2006 that focused on concentrations of chlorothalonil, dichlofluanid, and Irgarol in the major... |
|
|
Environmental risks associated with booster biocides leaching from spent anti-fouling paint particles in coastal environments.
Water Environ. Res. 86(12) , 2330-7, (2014) Boat maintenance facilities in coastal areas contribute a significant amount of antifouling paint particles (APP) to coastal environments. Very few studies have concentrated on the leaching of booster biocides embedded in old paint particles. Therefore, this ... |
|
|
Effects of seven antifouling compounds on photosynthesis and inorganic carbon use in sugar kelp Saccharina latissima (Linnaeus).
Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 63(3) , 365-77, (2012) Macroalgae depend on carbon-concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) to maintain a high photosynthetic activity under conditions of low carbon dioxide (CO(2)) availability. Because such conditions are prevalent in marine environments, CCMs are important for upholding ... |
|
|
Antifouling biocides in discarded marine paint particles.
Mar. Pollut. Bull. 60(8) , 1226-30, (2010) Antifouling paint fragments collected from marinas and leisure boat maintenance facilities and in the vicinity of abandoned boats have been chemically characterised. High concentrations of Cu (23-380mgg(-1)) and Zn (14-160mgg(-1)) in the samples (n=14) are co... |
|
|
A new simple method with high precision for determining the toxicity of antifouling paints on brine shrimp larvae (Artemia): first results.
Chemosphere 67(6) , 1127-32, (2007) The use of antifouling paints is the only truly effective method for the protection of underwater structures from the development of fouling organisms. In the present study, the surface to volume concept constitutes the basis for the development of a new and ... |
|
|
Coordination polymer adsorbent for matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of pesticides during analysis of dehydrated Hyptis pectinata medicinal plant by GC/MS.
Talanta 83(2) , 631-6, (2010) The coordination polymer [Zn(BDC)(H(2)O)(2)](n) was tested for extraction of pyrimethanil, ametryn, dichlofluanid, tetraconazole, flumetralin, kresoxim-methyl and tebuconazole from the medicinal plant Hyptis pectinata, with analysis using gas chromatography-m... |
|
|
Fate and distribution of pyrimethanil, metalaxyl, dichlofluanid and penconazol fungicides from treated grapes intended for winemaking.
Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 26(2) , 164-71, (2009) Tempranillo grapes were immersed in solutions of pyrimethanil, metalaxyl, dichlofluanid and penconazol fungicides at different concentrations for several different times. Determinations of the fungicide residues was carried out by GC-NPD, with an additional c... |